In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, companies face unprecedented challenges and opportunities. With technological advancements, accelerated globalization, and increasingly diverse consumer demands, traditional production and warehousing models can no longer fully meet the requirements of modern supply chain management. As a result, Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL) has emerged as a transformative supply chain management model, becoming instrumental for businesses seeking operational efficiency in complex market environments. But how exactly does 4PL operate?
Defining Fourth-Party Logistics
Fourth-Party Logistics refers to a logistics model that provides comprehensive, systematic supply chain solutions by integrating third-party logistics resources and other relevant assets. Its core value lies in helping businesses consolidate, optimize, and manage entire supply chains through strategic thinking and technological support. The concept was first introduced in 1996 by Kaplan and Norton and has since gained widespread adoption as a critical component of modern logistics.
The Role and Functions of 4PL
In supply chain management, 4PL serves as an efficiency enhancer. Specifically, it collaborates closely with third-party logistics (3PL) providers to expand market reach while improving the quality and efficiency of logistics services. In these partnerships, 4PL providers transcend the role of simple service vendors by offering technical support, supply chain strategy, market access capabilities, and project management services that enhance 3PLs' competitive advantages.
For instance, 4PL providers can leverage data analytics to help 3PL companies identify market trends and customer needs, enabling them to develop more targeted service offerings. This data-driven decision-making process not increases the flexibility and responsiveness of 3PL operations but also elevates the end-customer's logistics experience.
Key Differences Between 4PL and 3PL
While 4PL and 3PL share similarities, they differ fundamentally in scope and approach. Third-party logistics primarily focuses on concrete logistics services like transportation, warehousing, and distribution, whereas fourth-party logistics emphasizes holistic supply chain solutions with a systemic and strategic perspective.
Moreover, 3PL providers typically serve as operational executors of specific logistics tasks, while 4PL providers act as strategic navigators of the entire supply chain, offering more comprehensive services that span all supply chain components. In practice, businesses often require both 3PL and 4PL services simultaneously to achieve optimal logistics management.
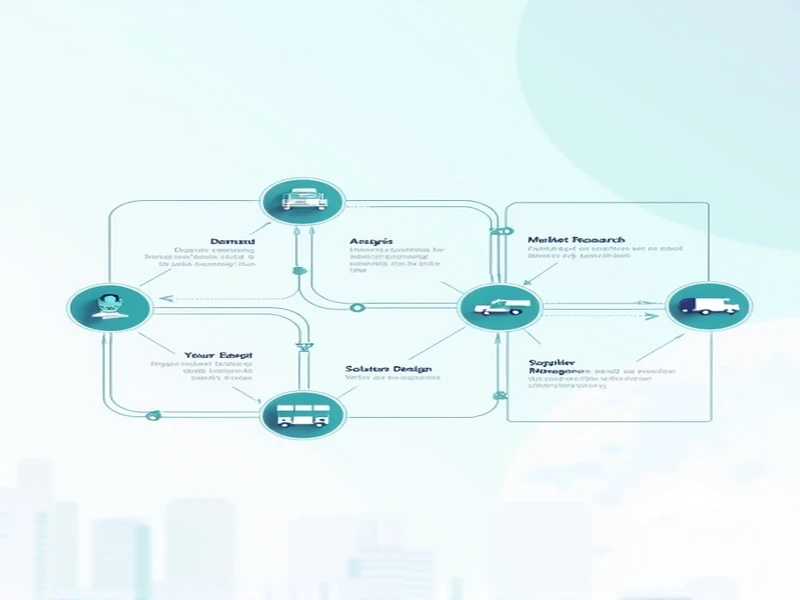
The Operational Mechanism of 4PL
The 4PL operational model typically involves several critical phases:
1. Demand Analysis and Market Research
Before implementing logistics solutions, 4PL providers conduct in-depth analysis of client requirements, market trends, and competitive landscapes. This process enables the development of tailored logistics solutions that better meet customer expectations.
2. Solution Design and Integration
Based on demand analysis, 4PL providers develop integrated logistics solutions encompassing transportation, warehousing, sorting, and distribution. These solutions balance cost efficiency with service quality improvements while leveraging multiple resources and technologies to deliver flexible, customized approaches.
3. Vendor Selection and Management
Following solution design, 4PL providers typically manage vendor selection processes. Through transparent bidding procedures, they identify suitable 3PL partners capable of meeting all solution requirements. This process includes evaluating potential vendors' capabilities, reputation, and service competencies.
4. Monitoring and Optimization
During implementation, 4PL providers continuously monitor and assess all operational aspects to ensure service delivery. Using real-time data feedback, they make necessary adjustments to optimize resource allocation and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Case Study: Practical Application
The value of 4PL becomes evident through real-world applications. Consider a major electronics manufacturer that decided to outsource its logistics operations to a 4PL provider amid rapidly changing market demands.
Expanding Outsourcing Scope
The company extended its outsourcing to include repair centers, central warehouses, regional distribution centers, return systems, and transportation—covering the entire supply chain. Detailed bidding documents specified requirements and standards for each component, with the 4PL provider offering expert recommendations based on market analysis.
Partner Selection
After thorough market research and transparent evaluation, the manufacturer selected optimal logistics partners. This choice enhanced supply chain coordination while improving service responsiveness and flexibility.
Results and Feedback
With 4PL support, the company achieved significant cost optimization and service quality improvements. Data showed a 20%+ increase in shipping efficiency and measurable gains in customer satisfaction—a success that strengthened the company's competitive position.
Future Outlook
As technology advances and markets evolve, 4PL will continue playing a pivotal role in modern supply chains. Key anticipated developments include:
1. Digital Transformation
With big data, cloud computing, and IoT advancements, 4PL will undergo digital transformation. Advanced tools will enable better data collection, analysis, and utilization for more scientific decision-making.
2. Sustainability Focus
As environmental consciousness grows, 4PL will increasingly contribute to sustainable development through resource optimization and waste reduction—benefiting both economics and ecology.
3. Global Expansion
With growing supply chain complexity, 4PL will expand internationally, integrating global resources to provide cross-border solutions that maintain competitive advantages.
4. Customer-Centric Approach
Future 4PL models will emphasize customer-centricity, delivering personalized solutions through deeper understanding of diverse and evolving consumer needs.
Conclusion
Fourth-Party Logistics has become indispensable in modern supply chains. Through strategic collaboration and integrated solutions, 4PL helps businesses thrive in competitive markets. As we stand at the forefront of supply chain transformation, adaptability and innovation remain key to sustainable success. By fully leveraging 4PL's potential, companies can better navigate complex environments and achieve long-term growth objectives.