In the complex landscape of international trade, particularly in the import and export of chemical products, manufacturers and trading companies frequently encounter a crucial document—the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). This specialized document, typically associated with hazardous chemicals, may also be required for certain non-hazardous goods during export processes.
Carriers and freight forwarders rely on MSDS documentation to make informed decisions about whether to accept shipping requests from consignors. The importance of MSDS cannot be overstated—it plays a vital role in ensuring the safety of personnel and property during transportation.
Understanding MSDS: A Comprehensive Safety Document
An MSDS is fundamentally a product safety document that covers multiple aspects including chemical properties, potential hazards, operational safety guidelines, and disposal instructions. Also known as a Chemical Safety Technical Specification or Chemical Safety Data Sheet, its primary purpose is to provide users with essential safety information and emergency response measures.
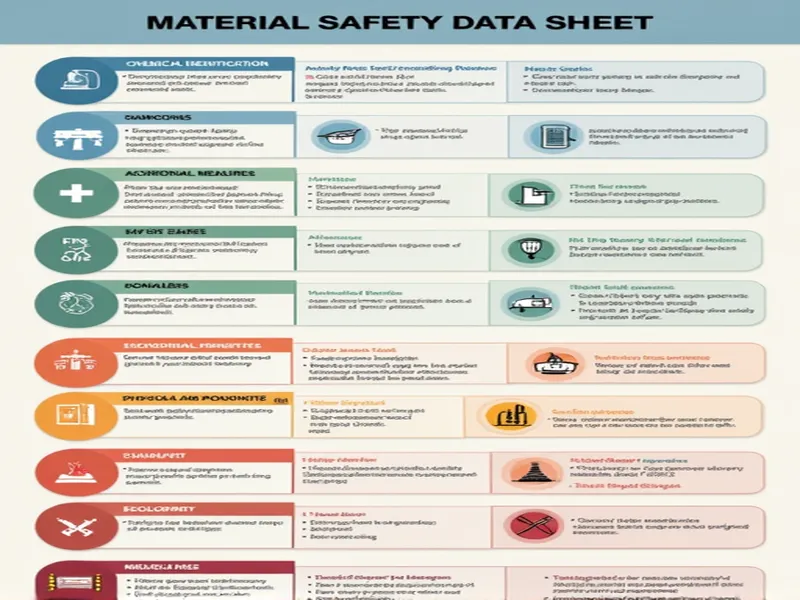
Typically, an MSDS contains 16 key sections designed to minimize risks, ensure personal safety, and protect the environment when handling chemicals:
- Chemical and company identification: Details the product name, intended use, and basic information about the manufacturer
- Composition information: Specifies the chemical components and their concentrations, which directly affect usage and storage requirements
- Hazard identification: Outlines potential risks, particularly health effects from exposure
- First aid measures: Critical emergency procedures for exposure or accidental inhalation
- Firefighting measures: Appropriate fire response protocols
- Accidental release measures: Procedures for spill containment and cleanup
- Handling and storage: Best practices for safe operation and transportation
- Exposure controls/personal protection: Recommended protective equipment for various working conditions
- Physical and chemical properties: Fundamental characteristics like melting point, boiling point, and density
- Stability and reactivity: Chemical behavior under different conditions
- Toxicological information: Health impact data
- Ecological information: Environmental impact assessment
- Disposal considerations: Safe handling of expired or unused chemicals
- Transport information: Shipping compliance guidelines
- Regulatory information: Legal compliance requirements
- Other information: Supplementary details and explanations
Global Trade Implications and Compliance Requirements
In international shipping processes, carriers frequently request MSDS documentation for safety assessments. Customs authorities may also require this document to verify compliance, while foreign clients often review MSDS for safety assurance. This demonstrates how MSDS significantly impacts both supply chain management and international business relationships in our increasingly globalized economy.
All personnel potentially handling such goods—including warehouse staff, loading workers, and transportation crews—should possess basic understanding of MSDS content. This knowledge provides operational guidance and becomes particularly critical during emergencies like package damage or chemical leaks. Without proper MSDS information, response teams may face dangerous delays or improper handling that could escalate incidents.
The catastrophic 2015 Tianjin port explosions serve as a sobering example. Improper handling led to devastating fires and explosions causing significant casualties and property damage. Effective use of MSDS documentation might have substantially mitigated these consequences.
Distinguishing MSDS from Other Certifications
It's crucial to recognize that MSDS differs fundamentally from test reports or identification certificates like the Air Transport Conditions Identification Report (commonly called "air transport certification"). While MSDS is prepared by chemical manufacturers or specialized companies, air transport certification must be issued by civil aviation authority-approved professional assessment institutions. Many companies confuse these documents during international trade, creating potential legal risks and financial losses.
By thoroughly understanding MSDS composition, purpose, and air transport certification systems, businesses can better ensure product safety and regulatory compliance in international trade. This responsibility extends beyond protecting company assets—it directly impacts customer trust and satisfaction.
As global trade evolves and technology advances, companies must proactively learn and apply such specialized knowledge to adapt to market changes and maintain competitive positions in international commerce.