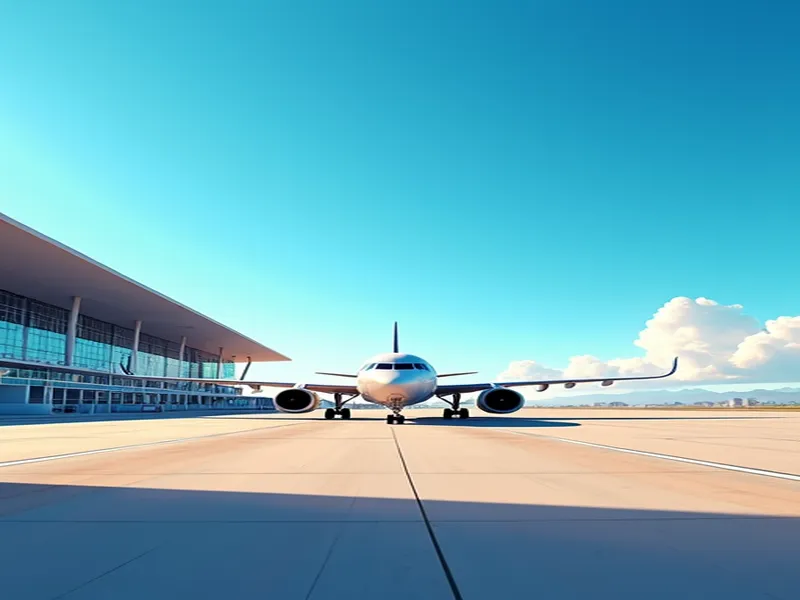
Málaga-Costa del Sol Airport, one of Andalusia's key transportation hubs in southern Spain, plays an indispensable role in domestic transport while maintaining significant importance in international aviation. The airport's development history reflects the economic growth and tourism boom of Málaga and the broader southwestern European region. This comprehensive analysis explores the airport's historical background, infrastructure, route network, service facilities, transport capacity, and economic contributions.
1. Historical Background
Málaga Airport's history dates back to 1919 when its modest facilities primarily served military aviation purposes. By the 1960s, Spain's political stabilization and tourism expansion transformed the airport into a civilian facility, particularly catering to growing numbers of European visitors. A significant upgrade came in 1971 with the inauguration of a new passenger terminal. Subsequent expansions in 1991, 2003, and 2010 progressively enhanced the airport's capacity to comfortably handle millions of annual passengers.
2. Infrastructure
Strategically located just 8 kilometers from Málaga's city center and proximate to popular resorts like Torremolinos and Nerja, the airport features a 3,200-meter runway (45m width) at 16 meters above sea level, capable of accommodating large aircraft. Three principal terminals serve distinct functions:
- Terminal 1: Processes non-Schengen international flights, serving as a global air bridge.
- Terminal 2 (Pablo Ruiz Picasso Terminal): Operational since 1991 with modern upgrades, handling Schengen international and domestic flights.
- Terminal 3: The largest facility (250,000 sqm) since 2010, featuring 264 boarding gates, capacity for 9,000 passengers/hour, plus commercial lounges, dining options, and duty-free shopping.
The terminals' efficient layout and seamless transfer services effectively manage peak passenger flows.
3. Route Network
Málaga Airport maintains extensive connections to major Spanish cities (Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia) and international destinations across Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and North America. With approximately 2,000 regular flights, seasonal routes significantly expand during summer tourism peaks.
3.1 Key Airlines
Major carriers including Iberia, easyJet, Ryanair, and British Airways utilize Málaga as a strategic hub, facilitating both passenger transport and regional tourism development.
3.2 Primary Routes
Frequent connections include London, Paris, Frankfurt, and Amsterdam, alongside routes to Casablanca, Istanbul, and Dubai. The airport's expanding global connectivity reflects its growing international prominence.
4. Service Facilities
The airport prioritizes passenger experience through:
- Dining: Diverse options from traditional Spanish fare to international cuisine
- Retail: Extensive duty-free shopping with global brands
- Accessibility: Multilingual staff and wheelchair services ensure inclusive travel
5. Transport Capacity
2014 operational data highlights the airport's scale:
- Passenger volume: 13,748,976
- Flight movements: 108,261
- Cargo handled: 2,498 tons
6. Economic Impact
As Andalusia's economic engine, the airport generates substantial revenue for local hospitality, retail, and service sectors. With global tourism rebounding, Málaga continues expanding international routes to stimulate regional growth.
Ranked as Spain's fourth-busiest airport, Málaga-Costa del Sol leverages its geographic advantage and continuous infrastructure improvements to strengthen global connections. As travel markets recover, the airport is poised to enhance its role in international aviation networks while maintaining efficient, passenger-focused operations.