In today's logistics industry, warehouse picking efficiency is not only a core element of internal warehouse operations but also an indispensable link in the entire supply chain. As market demands continue to evolve and competition intensifies, modern enterprises face numerous challenges, including how to meet customers' personalized needs and reduce operational costs. In this context, warehouse managers urgently need to explore effective picking strategies to ensure timely order fulfillment and service quality, thereby enhancing overall corporate competitiveness.
I. Fundamental Concepts of Order Picking
In warehouse operations, order picking is one of the core processes, referring to warehouse staff selecting products from inventory according to customer orders for shipment. The picking process involves not only locating the required items but also checking product conditions, packaging, labeling, and final dispatch. Therefore, order picking is not just a basic warehouse operation but also has profound impacts on customer satisfaction, overall warehouse efficiency, and corporate profitability.
In practice, picking operations typically account for 55% of warehouse labor costs. This means most human resources in warehouses are concentrated on picking activities. Consequently, improving picking efficiency is an effective way to reduce operational costs. To achieve this goal, warehouse managers need to conduct in-depth analysis and research on the picking process to identify appropriate improvement solutions.
II. Diversity of Picking Methods
When selecting picking methods, one cannot rely solely on experience to judge their effectiveness. The key lies in matching warehouse characteristics with actual needs. Different warehouses, products, and order characteristics lead to varied picking methods. Common picking methods include:
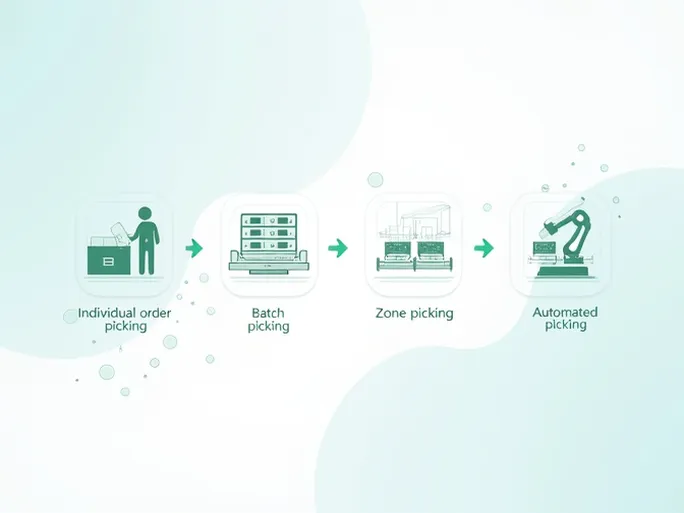
- Discrete Order Picking: Suitable for scenarios with large order volumes but relatively few SKU types. In this method, pickers can select items one by one according to customer orders, achieving efficient picking operations.
- Batch Picking: Ideal for situations with massive order volumes. This method emphasizes picking all items first and then sorting them by order. By optimizing travel distance and time, picking efficiency can be significantly improved.
- Zone Picking: The warehouse is divided into multiple zones, with pickers assigned to specific areas. This method reduces pickers' travel time and enhances efficiency.
- Wave Picking: Suitable for environments with numerous SKUs but low demand for each. By processing similar or identical SKUs collectively, pickers can improve single-trip efficiency.
- Automated Picking: With technological advancements, more companies are adopting automation. Using equipment like robotic carriers and automated storage systems can dramatically increase picking efficiency while reducing labor costs.
Each picking method has its advantages and disadvantages. In practical applications, warehouse managers should comprehensively consider factors such as warehouse characteristics, product types, customer needs, and order features to select the most suitable method.
III. Scientific Analysis of Picking Strategies
Designing effective picking strategies should closely align with order structures and product characteristics to ensure they meet actual operational needs. In e-commerce warehouse environments, the following aspects should be considered:
- Identical Order Structures: When orders contain many repeated SKUs, a secondary sorting strategy can be applied. This allows pickers to handle orders with identical SKUs and quantities collectively, improving packing efficiency—especially effective when demand forecasting is accurate.
- Diverse Order Structures: For orders with numerous SKU types and few items per order, analysis based on average items per order is crucial. For single-item protection, zone picking can ensure order accuracy, while small items can use secondary sorting to minimize time waste.
- Large Items: Typically require a combination of picking methods to achieve optimal efficiency. Given their size and weight, equipment like forklifts and conveyors can be used to reduce manual labor costs.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: Leveraging data analysis to monitor and evaluate order flows and picking efficiency in real time. Through data mining, warehouse managers can quickly identify bottlenecks and make appropriate adjustments.
When formulating picking strategies, special considerations should be given to hazardous materials, fragile items, and seasonal products, with corresponding regulations established to ensure safe, efficient, and smooth warehouse operations.
IV. Practical Measures to Enhance Picking Efficiency
To improve warehouse picking efficiency, companies should implement the following practical measures:
- Optimize Warehouse Layout: The layout directly impacts picking efficiency. Scientific design of entrances, exits, shelf placements, and aisle widths can significantly reduce pickers' travel time. Additionally, storing high-mobility items nearby, categorizing easily accessible goods, and using clear labeling can enhance visibility and efficiency.
- Plan Efficient Picking Routes: Route planning is crucial in picking. Warehouse managers can determine optimal sequences based on product categories to minimize movement distance. Wave picking, which groups similar items, can also boost efficiency.
- Paperless Transformation: Traditional picking often relies on paper orders, leading to delays and errors. Adopting digital tools like wireless terminals and voice systems improves real-time accuracy and reduces labor intensity.
- Designate Sorting Areas: Establishing dedicated sorting zones within warehouses shortens pickers' movement time, allowing them to focus on picking. This measure also integrates picking, packing, and shipping to improve overall efficiency.
- Assembly Line Operations: Combining "goods-to-person" picking with automation reduces errors and enhances workflow continuity. This requires integrating IT with production processes and using data monitoring to optimize resource utilization.
- Continuous Evaluation and Adjustment: Regularly monitor picking metrics and adjust strategies dynamically. Quarterly or annual reviews using sales data and efficiency reports help identify issues and implement improvements.
Conclusion: There are numerous ways to enhance traditional warehouse picking efficiency, with the key lying in strategic planning and implementation. Through scientific strategy design and systematic optimization, companies can better adapt to the rapid development of modern logistics and market competition. For warehouses committed to improving operational efficiency, maintaining innovative and flexible thinking is the path to excellence. In this ever-evolving industry, only continuous exploration and practice can lead to long-term success. This article aims to provide valuable insights for warehouse managers and guide the transformation and advancement of the logistics sector.