Introduction
In today's competitive market landscape, product quality directly determines a company's survival and growth. However, maintaining product integrity throughout warehousing and logistics operations remains a significant challenge for many businesses. Warehouse quality control serves not only as the critical link in preserving product condition across supply chains but also as a powerful tool for enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. This article explores the definition, objectives, key methodologies, and implementation strategies of warehouse quality control to provide actionable management insights.
I. Definition and Significance of Warehouse Quality Control
1. Definition
Warehouse quality control refers to the systematic measures implemented during storage, handling, packaging, and distribution to prevent product damage, deterioration, or loss. This comprehensive process spans inventory receipt, dispatch, and environmental monitoring, aiming to minimize quality issues throughout warehouse operations.
2. Role in Supply Chain Management
Warehouses serve as vital intermediaries in supply chains, bridging manufacturers with distributors, retailers, and end consumers. Effective quality control ensures product integrity, directly impacting supply chain reliability and efficiency. Quality lapses can trigger production halts, logistical delays, and customer complaints, potentially damaging brand reputation and profitability.
Thus, warehouse quality control transcends mere product preservation—it enhances overall supply chain performance, reduces operational costs, and elevates customer experiences. Through scientific management, warehouses can effectively coordinate supply chain segments, ensuring damage-free product transit and preventing unnecessary losses.
II. Core Objectives of Warehouse Quality Control
Beyond preventing product damage, warehouse quality control pursues deeper strategic goals:
- Product Consistency: Environmental controls (temperature, humidity, etc.) maintain product stability throughout storage and transit.
- Customer Satisfaction: Meeting quality expectations enhances shopping experiences and fosters brand loyalty.
- Cost Reduction: Minimizes returns and repairs stemming from quality issues.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Optimized inventory turnover reduces storage-related damages and delays.
- Brand Competitiveness: Superior product quality builds consumer trust in increasingly quality-conscious markets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to standards mitigates legal risks and financial penalties.
III. Key Methodologies and Technologies
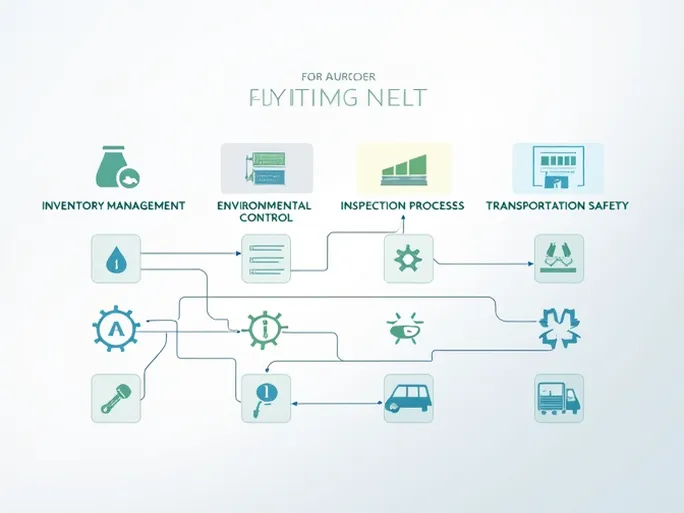
1. Precision Inventory Management
Barcode and RFID technologies enable accurate tracking and management of inventory items, forming the foundation for quality assurance.
2. Storage Environment Control
Climate-sensitive products require specialized monitoring equipment and regular inspections. Proper product segregation and stacking prevent cross-contamination and damage.
3. Handling Process Optimization
Employee training and appropriate handling equipment minimize transit damage, complemented by protective packaging solutions.
4. Rigorous Quality Inspections
Pre-shipment inspections and periodic sampling create critical quality checkpoints to identify and resolve issues proactively.
5. Warehouse Safety Systems
Fire prevention measures and surveillance systems ensure operational continuity and protect both personnel and inventory.
IV. Implementation Strategies
1. Total Quality Management (TQM)
This organization-wide approach engages all employees in continuous quality improvement through feedback loops and process refinement.
2. Preventive Management
Proactive measures—from rigorous intake inspections to environmental maintenance—preempt quality issues before they occur.
3. Detail-Oriented Operations
Meticulous attention to inventory accuracy and handling procedures, reinforced through regular training, establishes sustainable quality standards.
By implementing these best practices, companies can simultaneously enhance warehouse efficiency and deliver superior customer experiences—key differentiators in competitive markets.