Parallel import cars, also known as non-authorized imports, refer to vehicles purchased directly from overseas markets by traders and introduced to China without brand manufacturer authorization. These cars differ from traditional "China-spec" vehicles sold through official brand channels domestically. Parallel imports have gradually gained popularity among consumers, particularly those with higher requirements for vehicle performance, appearance, and personalized configurations.
I. Sources of Parallel Import Vehicles
Parallel import cars typically originate from multiple countries and regions including the United States, Japan, Europe, and the Middle East. Vehicles from different markets vary in price, configuration, and performance. For instance, U.S. market vehicles often feature higher specifications at relatively lower prices, while certain European models may maintain price advantages due to brand prestige. These differences provide consumers with more options and make parallel imports stand out in the domestic market.
II. Characteristics of Parallel Import Cars
- Price Advantage: Parallel imports are generally cheaper than their China-spec counterparts, primarily due to reduced middleman costs and manufacturer pricing pressures, allowing consumers to access high-quality vehicles at lower prices.
- Wider Model Selection: Covering multiple global markets, parallel imports offer access to special editions and configurations often unavailable domestically, including limited editions and region-specific models.
- Faster Delivery: With many models available as ready stock, parallel imports enable quicker vehicle collection—an attractive feature for urgent buyers.
- Customization Options: Parallel imports typically provide more diverse configuration choices, allowing consumers to personalize interiors, exteriors, tech features, and powertrains to suit individual preferences.
III. Current Status of Private Vehicle Imports
As globalization progresses, individual consumers—particularly overseas students and workers—are increasingly exploring parallel imports to acquire cost-effective vehicles. However, private imports involve complex procedures requiring compliance with strict regulations, including valid foreign residency status and adherence to Chinese environmental and safety standards for successful domestic registration.
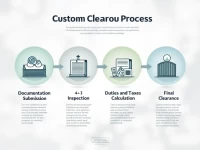
IV. Taxes and Procedures
Importing vehicles into China incurs several taxes calculated based on engine displacement:
- Customs Duty: Levied on the transaction price, with higher rates for larger engines.
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): Applied to the price increment during importation.
- Consumption Tax: An additional levy on luxury or high-displacement vehicles.
The clearance process requires multiple documents including import certificates, inspection reports, conformity certificates, purchase invoices, and electronic information. Notably, used vehicle imports face strict prohibitions under current policies.
V. Policy Changes and Future Outlook
To stimulate market growth, China has gradually relaxed parallel import regulations by simplifying quantity limits and certification requirements. These measures aim to enhance market vitality and consumer choice while prompting brand manufacturers to improve service offerings—bolstering buyer confidence in parallel imports.
VI. Consumer Considerations
Prospective buyers should evaluate several factors:
- Budget: While generally cheaper, total costs including taxes must be considered.
- Brand/Model: Select options aligning with personal preferences and needs.
- After-Sales Service: Verify available support networks for maintenance and repairs.
- Compliance: Ensure vehicles meet all Chinese regulatory standards to avoid legal issues.
VII. Conclusion
Parallel imports represent an innovative purchasing channel that expands consumer choice and intensifies market competition. Despite procedural complexities, ongoing policy improvements suggest a promising future for this sector. Consumers should conduct thorough research to mitigate risks associated with information asymmetry when considering parallel import vehicles.