In modern logistics and warehouse management, pallets serve as an indispensable component, playing a crucial role not only in supporting goods during transportation but also in enhancing operational efficiency, reducing manual labor, and ensuring cargo safety. Among various pallet types, 2-Way Pallets and 4-Way Pallets stand out as the most common options, each offering distinct design features, functionalities, and application scenarios to meet diverse business needs.
2-Way Pallets: Strength and Simplicity
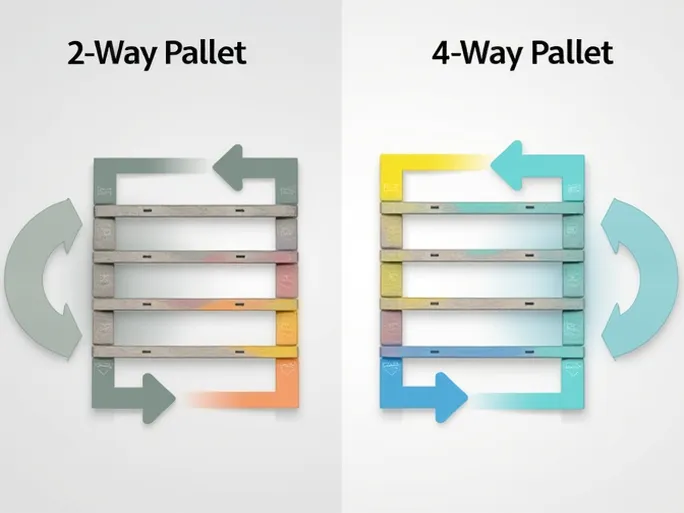
The structural design of 2-Way Pallets limits forklift operation to two directions - allowing entry only from the front and back. This simplified design streamlines manufacturing processes while enhancing load-bearing capacity. Typically constructed with more robust materials, these pallets excel in heavy-load environments such as industrial production lines or large-scale warehouses.
However, this configuration reduces operational flexibility in dynamic or space-constrained environments, potentially decreasing material handling efficiency. The restricted access points may create bottlenecks in fast-paced logistics operations where quick turnaround is essential.
4-Way Pallets: Flexibility and Efficiency
4-Way Pallets offer superior flexibility with forklift access from all four directions, allowing operators to choose the most efficient loading approach based on situational requirements. This versatility proves particularly valuable in urban distribution centers and automated warehouses where rapid goods turnover is critical.
The multidirectional access significantly reduces waiting times and improves workflow efficiency, making these pallets the preferred choice for advanced warehouse management systems and logistics providers focused on optimizing operational throughput.
Selection Criteria for Optimal Performance
Choosing between pallet types requires careful analysis of multiple factors beyond basic functionality:
- Load characteristics: Weight distribution and cargo type
- Operational environment: Warehouse layout and space constraints
- Throughput requirements: Handling frequency and speed demands
- Cost considerations: Initial investment versus long-term efficiency gains
While 4-Way Pallets generally offer greater flexibility, 2-Way Pallets may prove more suitable for specialized applications requiring exceptional load capacity. Businesses should establish comprehensive evaluation frameworks to match pallet characteristics with specific operational requirements.
Sustainability Considerations
As environmental consciousness grows in supply chain management, pallet manufacturers are increasingly offering eco-friendly alternatives made from recycled or biodegradable materials. These sustainable options not only align with global environmental initiatives but also enhance corporate social responsibility profiles - particularly important for international trade operations where environmental compliance affects brand reputation.
Modern businesses must therefore balance traditional selection criteria with emerging sustainability requirements when implementing pallet solutions.
Conclusion
Both 2-Way and 4-Way Pallets present unique advantages and limitations. The optimal choice depends on careful consideration of load capacity, movement flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact. Proper pallet selection can dramatically improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure cargo safety throughout the supply chain - ultimately strengthening market competitiveness in today's demanding logistics landscape.