In today's supply chain management, warehouse configuration has become increasingly crucial. Have you ever wondered why an efficient warehouse stands out in a rapidly changing market? Warehouse configuration goes beyond mere physical space arrangement—it represents a systematic approach to logistics facilities, storage systems, equipment, staffing, and operational workflows. By strategically organizing the production environment, warehouses can significantly enhance order fulfillment speed and accuracy while gaining a competitive edge.
I. Core Objectives of Warehouse Configuration
The primary goals of warehouse configuration include:
- Reducing delivery cycles: Through optimized layouts and workflows to minimize inventory turnover time and accelerate order processing.
- Maximizing space utilization: Implementing scientific storage methods and location optimization to make the most of limited space.
- Lowering operational costs: Streamlining processes and eliminating unnecessary inventory buildup for better cost control.
- Enhancing operational efficiency and productivity: Utilizing automation and proper staffing to improve performance while reducing labor intensity.
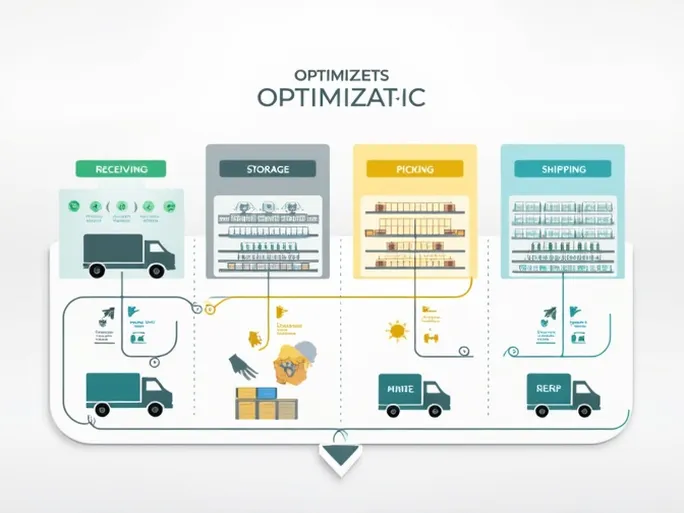
II. Strategic Zone Planning in Warehouses
Modern warehouses consist of several critical zones, each playing a vital role in the overall logistics chain.
1. Receiving Area
As the first step in warehouse operations, receiving area placement is critical. Ideally positioned near main entrances to minimize material transport time and costs, this zone requires unloading docks, lifting equipment, and automated sorting systems for efficient management. All incoming goods must undergo thorough quality and quantity inspections to meet storage standards and identify discrepancies promptly.
In the e-commerce era, receiving areas must handle massive product inflows efficiently. Barcode scanning technology and automated conveyor systems accelerate intake processes. Growing consumer demands make accuracy and speed increasingly important, necessitating real-time data monitoring and digital management solutions.
2. Storage Zone
The warehouse's heart, the storage area's efficiency depends on appropriate system selection. Layout and organization should adapt to product characteristics and market demands. High-turnover items benefit from shelving systems that maximize storage density and accessibility, while bulk goods require pallet storage for stability and safety.
Thoughtful aisle design ensures smooth equipment movement and prevents congestion. Modern inventory management systems enable real-time monitoring and location optimization. Specialized storage solutions, like temperature-controlled environments, cater to pharmaceuticals and perishable goods.
3. Picking Zone
This critical order fulfillment component requires designs that minimize worker travel through optimal shelf placement and picking routes. Multiple sub-zones accommodate different picking methods (single-item, batch picking) to match customer needs.
Advanced technologies like voice-picking systems and RFID ensure accuracy and timeliness. Data analysis tools predict high-demand items from historical patterns, allowing proactive stock positioning. Emerging automation solutions, including AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles), reduce errors while increasing flexibility and safety. Future systems may leverage AI to dynamically optimize product placement based on order patterns.
4. Shipping Area
The final processing stage requires meticulous organization to guarantee timely, accurate deliveries. Design considerations include transportation access, sorting efficiency, and loading workflows. Effective load management enhances transport efficiency while minimizing errors and delays.
Real-time tracking systems and communication with carriers ensure accurate information transfer. Smart loading equipment boosts efficiency while reducing human error risks, and customer notification systems improve service experiences.
III. Warehouse Optimization Strategies
Effective warehouse management extends beyond physical layout to incorporate data systems and technology integration:
- Enhanced data management: Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) track inventory movements, analyze turnover patterns, and identify optimization opportunities.
- Smart technology implementation: AI and IoT solutions enable responsive, adaptive operations that adjust to changing conditions.
- Workforce development: Regular training ensures staff proficiency with modern systems and processes.
- Continuous process improvement: Regular evaluations using LEAN/VSM methodologies eliminate inefficiencies.
IV. Navigating Operational Challenges
Warehouses face numerous challenges from market volatility to supply chain disruptions. Effective strategies include:
- Adaptive inventory management: Dynamic replenishment systems and safety stock buffers address demand fluctuations.
- Comprehensive contingency planning: Detailed protocols for equipment failures, natural disasters, and other emergencies.
- Supply chain collaboration: Information sharing with suppliers and transporters enables coordinated responses.
- Multimodal distribution: Flexible shipping options ensure continuity during disruptions.
Optimized warehouse configuration forms the foundation of efficient supply chains. By refining every operational aspect, businesses gain significant competitive advantages. As technology advances and market demands evolve, warehouse management will face greater challenges—but also unprecedented opportunities. Success will depend on organizational agility and innovation in pursuing sustainable, high-performance operations.