In today's globalized economy, international money transfers have become an essential part of personal and business activities. When it comes to cross-border transactions, the SWIFT/BIC code plays a pivotal role in ensuring funds are transferred accurately and efficiently. This article explores the intricacies of SWIFT/BIC codes, using BCECCLRFXXX as an example, to shed light on their critical function in global finance.
The Origin and Significance of SWIFT/BIC Codes
SWIFT, which stands for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, was established in 1973 in Belgium. Its primary purpose was to provide a secure, fast, and reliable messaging system for financial institutions worldwide. To facilitate seamless communication between international banks, SWIFT introduced a standardized bank identification system known as the SWIFT/BIC code.
The BIC (Bank Identifier Code), commonly referred to as the SWIFT code, serves as a unique identifier for banks within the global banking network. These codes enhance transaction security while significantly improving the efficiency of international transfers. By adopting a standardized format, SWIFT/BIC codes enable smooth financial communication, allowing banks to instantly recognize transaction pathways.
Breaking Down the SWIFT/BIC Code Structure
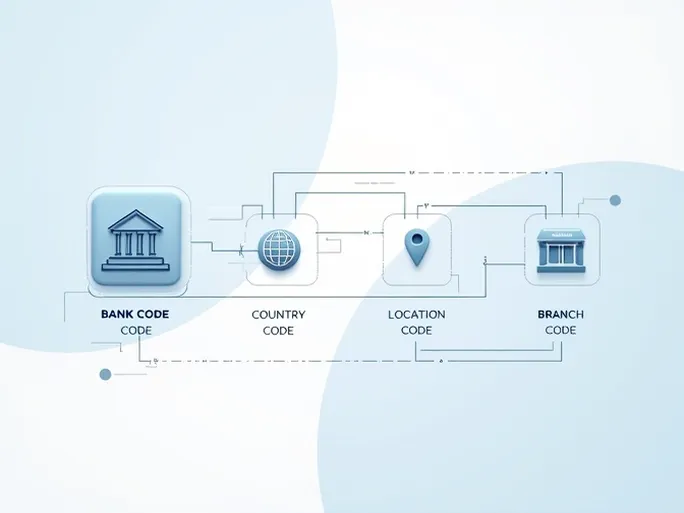
A standard SWIFT/BIC code consists of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters. Using BCECCLRFXXX as an example, let's examine each component:
- Bank Code (BCEC): The first four characters identify the specific bank. In this case, "BCEC" represents Banco Central de Chile.
- Country Code (CL): The following two letters denote the bank's country of origin. "CL" stands for Chile, as per international standards.
- Location Code (RF): These two characters specify the bank's headquarters or primary location. "RF" indicates the central bank's operational base.
- Branch Code (XXX): The final three characters (optional) identify specific branches. "XXX" typically refers to the bank's main office.
Practical Applications of SWIFT/BIC Codes
SWIFT/BIC codes are indispensable in international wire transfers. Providing the correct code ensures funds reach the intended recipient without delays or errors. An incorrect code may result in misdirected payments, processing delays, or even lost transactions. Therefore, verifying the SWIFT/BIC code before initiating a transfer is crucial.
Best Practices for Using SWIFT/BIC Codes
- Double-Check the Code: Always verify the SWIFT/BIC code against official bank records before submission. Obtain the latest code directly from the bank's website or customer service.
- Confirm with the Recipient: For first-time transfers, cross-check the code with the recipient's bank to ensure accuracy, especially for large transactions.
- Refer to Bank Statements: Bank statements often include the correct SWIFT/BIC code along with other relevant account details.
- Verify Branch-Specific Codes: If using a branch-specific code, confirm that it matches the recipient's account location.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult your bank or a financial advisor if you encounter uncertainties regarding SWIFT/BIC codes.
Common Misconceptions About SWIFT/BIC Codes
Several misconceptions can complicate international transfers:
- Assuming Similar Codes Are Interchangeable: Banks may have similar names or codes, but each code is unique. Always verify the exact code for the intended recipient.
- Overlooking Branch-Specific Codes: Some branches require distinct SWIFT/BIC codes. Using the main office code for a branch transaction may cause failures.
- Ignoring Code Updates: Banks occasionally update their SWIFT/BIC codes. Failing to verify the latest code can lead to transfer errors.
- Relying on Unverified Sources: Only obtain SWIFT/BIC codes from official bank channels to prevent fraud or misinformation.
The Step-by-Step Process of International Transfers
Understanding SWIFT/BIC codes is fundamental to executing successful international transfers:
- Select a Transfer Method: Choose between bank branches, online banking, or mobile apps for initiating the transfer.
- Gather Required Information: Prepare identification documents, recipient details (SWIFT/BIC code, account number, name), and transfer amount.
- Complete the Transfer Form: Enter all details accurately, ensuring the SWIFT/BIC code matches the recipient's bank.
- Choose a Payment Method: Select a funding source with sufficient balance for the transfer.
- Review and Submit: Confirm all details before submission and retain the transaction receipt.
- Monitor the Transfer: Track the transfer status using your bank's tools or customer service.
Resolving Issues and Filing Complaints
If problems arise during a transfer, take the following steps:
- Contact Your Bank: Reach out to customer service immediately with transaction details and evidence.
- Track the Transfer: Monitor the payment status to determine if delays or errors occurred.
- Document Communications: Keep records of all interactions with the bank, including dates and representatives' names.
- Seek Legal Advice: If unresolved, consult legal professionals or consumer protection agencies for assistance.
Conclusion
SWIFT/BIC codes are the backbone of international banking, enabling secure and efficient cross-border transactions. By mastering their structure and application, individuals and businesses can minimize errors and ensure smooth financial operations. Always verify the latest codes and adhere to best practices to safeguard your international transfers.