In global financial transactions, security and efficiency remain paramount concerns. Among the critical elements facilitating international money transfers is the SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) code, a standardized identifier that ensures funds reach their intended destination.
Taking Banco de Chile as an example, let's examine how SWIFT/BIC codes function and why their proper use is essential for seamless cross-border transactions.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
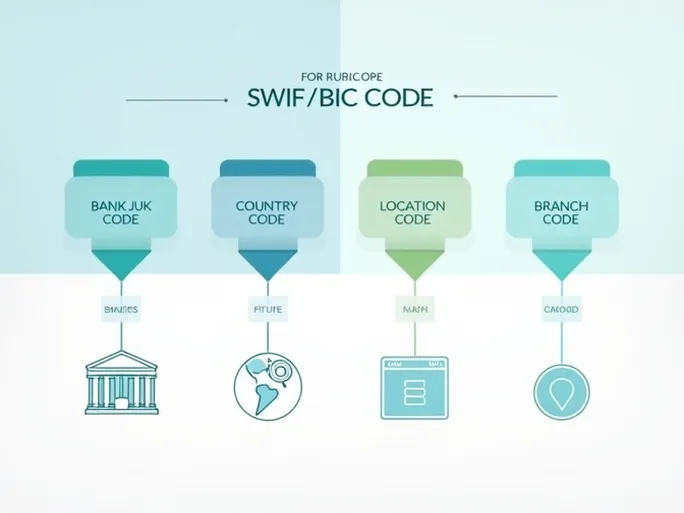
A SWIFT/BIC code consists of 8 to 11 characters, each conveying specific information. Using Banco de Chile's code "BCHICLRMCUS" as illustration:
- Bank Code (BCHI): Identifies Banco de Chile
- Country Code (CL): Indicates Chile as the bank's location
- Location Code (RM): Specifies the bank's headquarters
- Branch Code (CUS): Identifies specific branches (XXX denotes headquarters)
Banco de Chile's SWIFT Code Details
- SWIFT Code: BCHICLRM
- Branch Code: CUS
- Bank Name: Banco de Chile
- Address: Ahumada 251
- City: Santiago
Essential Verification Steps
Before initiating international transfers, financial experts recommend confirming these critical details:
- Bank Name: Ensure the SWIFT code matches the recipient's bank name precisely
- Branch Specificity: Verify whether the transaction requires a specific branch code
- Country Accuracy: Confirm the country code aligns with the recipient bank's location
Proper understanding and application of SWIFT/BIC codes significantly reduces transaction errors and delays. This knowledge proves invaluable for both individual and corporate clients engaged in international banking operations.
As financial systems continue to globalize, mastery of these fundamental banking identifiers remains crucial for secure and efficient cross-border transactions.