In the modern financial system, international bank transfers have become an essential component of daily transactions for both individuals and businesses. As the global economy continues to expand, cross-border transactions are occurring with increasing frequency, bringing the critical issue of ensuring secure and efficient fund transfers to the forefront. The use of SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) codes plays a particularly vital role in this process, serving not only as a bank's "identity card" but also as a key element in guaranteeing the smooth flow of funds.
This article explores the function of SWIFT codes in greater depth, with special attention to ensuring accurate information input when sending international transfers to STANDARD CHARTERED BANK (SINGAPORE) LIMITED, thereby achieving efficient and secure fund transfers.
What Is a SWIFT Code?
A SWIFT code, also known as a Bank Identifier Code (BIC), is a unique combination of letters and numbers used by banks and financial institutions worldwide. Typically consisting of 8 to 11 characters, it serves to uniquely identify a specific bank and its branch. The SWIFT system itself provides a secure channel for international banks to exchange information and funds, ensuring transactions are both swift and secure.
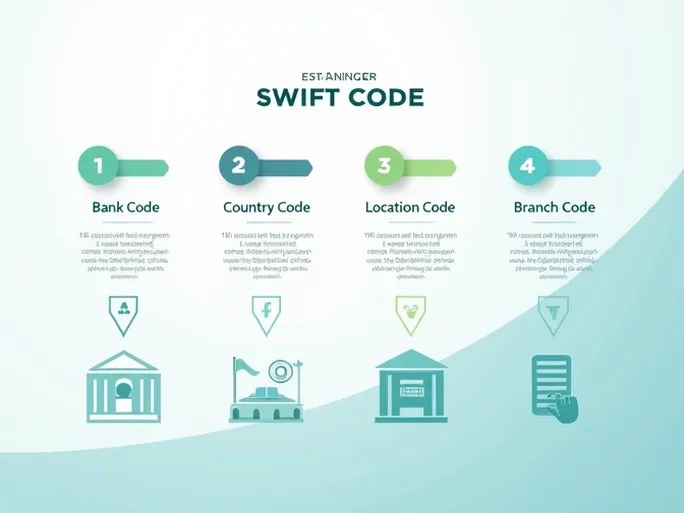
Understanding the structure of a SWIFT code is crucial for its proper use. Generally, a SWIFT code is divided into the following components:
- Bank code: The first four letters represent the bank's name.
- Country code: The next two letters indicate the country where the bank is located.
- Location code: The following two characters denote the city or region.
- Branch code (optional): The final three characters identify a specific branch.
For example, the SWIFT code for STANDARD CHARTERED BANK (SINGAPORE) LIMITED is SCBLSG22EQI, where "SCBL" represents the bank name "STANDARD CHARTERED," "SG" is the country code for Singapore, "22" is the location code, and "EQI" refers to a specific branch.
The Importance and Challenges of International Transfers
International transfers play a significant role in business transactions, tuition payments, personal support, and more. In an increasingly interconnected world, the demand for cross-border remittances continues to grow. However, despite the proliferation of transfer channels, many individuals and businesses still face numerous challenges during the process.
For instance, errors in transfer information can lead to failed transactions, delays, or even permanent loss of funds. An incorrect SWIFT code may result in funds not reaching the intended recipient's account or being mistakenly transferred to another bank. In some cases, recovering these funds can be a time-consuming and labor-intensive process.
Ensuring SWIFT Code Accuracy
When conducting an international transfer, verifying the accuracy of the SWIFT code is paramount. Below are practical recommendations to ensure error-free transactions:
- Confirm the bank name: Ensure the bank name matches the recipient's bank exactly, especially since some banks operate in multiple countries.
- Verify the SWIFT code: Cross-check the code through the bank's official website, bank personnel, or reliable third-party sources.
- Check branch details: If using a branch-specific SWIFT code, confirm it aligns with the recipient's account branch.
- Validate address information: Ensure accompanying details like street, city, and postal code are correct.
Standardizing the Transfer Process
Establishing a standardized transfer process can minimize errors. When sending funds to STANDARD CHARTERED BANK (SINGAPORE) LIMITED, follow these steps:
- Gather all necessary information, including the recipient's account number and SWIFT code.
- Use secure transfer channels, such as reputable banks or financial service providers.
- Maintain records of transaction details for future reference.
- Monitor the transfer status through available tracking services.
Implications for Businesses
For businesses, the efficiency of international transfers directly impacts market expansion, supply chain management, and client relations. Companies must prioritize cost control, transfer speed, and establishing reliable financial partnerships abroad.
By using correct SWIFT codes, businesses can expedite fund transfers, mitigating contractual risks and commercial losses due to delays. Standardized processes and accurate information enhance financial efficiency and foster trust, facilitating deeper international collaboration.
Conclusion
As globalization progresses, the demand for cross-border transfers will continue to rise. SWIFT codes remain a cornerstone of international banking, and their accuracy is critical for both individuals and businesses. When transferring funds to STANDARD CHARTERED BANK (SINGAPORE) LIMITED, using the correct SWIFT code (SCBLSG22EQI) minimizes delays and potential losses.
Whether for personal or business purposes, establishing rigorous verification processes—from confirming recipient details to monitoring transfer status—is essential. Through meticulous preparation and careful execution, users can navigate the complexities of global finance with confidence, ensuring seamless and secure international transactions.