In today's globalized financial landscape, where international money transfers and cross-border transactions have become commonplace, understanding SWIFT/BIC codes has never been more crucial. Many individuals and businesses have experienced the confusion of correctly completing bank details for international payments—a common challenge given the diversity of banking systems across different countries and regions. The SWIFT/BIC code system was specifically designed to address this challenge, ensuring efficient and secure international fund transfers.
What Exactly Are SWIFT/BIC Codes?
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) represents the standardized protocol for financial messaging between banks and financial institutions worldwide. The BIC (Bank Identifier Code) serves as the unique identification code for specific banks within this system. Far from being random character strings, SWIFT/BIC codes follow a precise structure where each segment carries specific meaning, forming the foundation for secure and efficient interbank communication.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
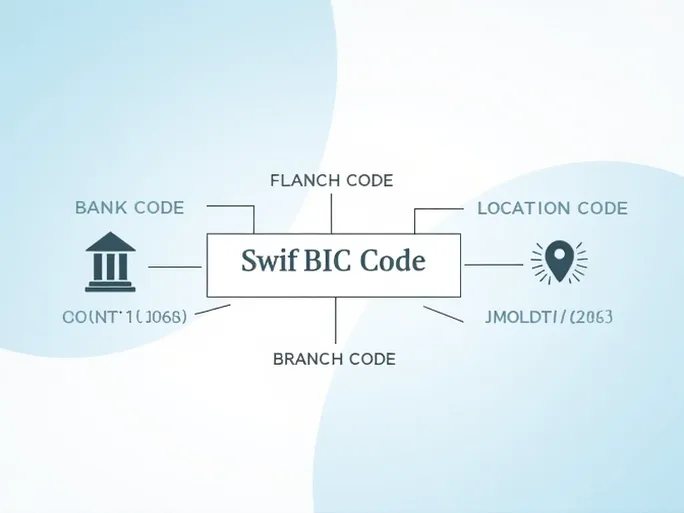
Consider the example of BANCO CENTRAL DEL PARAGUAY's SWIFT/BIC code: BCPAPYPXGON . This code breaks down into four distinct components:
- Bank Code (BCPA): The first four letters identify the bank—in this case, representing BANCO CENTRAL DEL PARAGUAY. This allows immediate recognition of the financial institution.
- Country Code (PY): The subsequent two letters indicate the bank's home country using international standard codes—PY for Paraguay in this example.
- Location Code (PX): These two characters specify the bank's headquarters location, often corresponding to a particular city.
- Branch Code (GON): The final three digits identify specific branches. A generic "XXX" ending typically denotes the bank's main office rather than a particular branch.
Critical Verification Steps for International Transfers
Using the correct SWIFT code proves essential for successful international transactions. Before initiating any transfer, carefully verify:
- Exact Bank Name: Ensure the recipient bank's name matches precisely with official records, as similarly named institutions across countries may cause confusion.
- Specific Branch Information: When using branch-specific codes, confirm the exact branch location matches the recipient's details.
- Country Verification: With financial institutions operating globally, always cross-check that the SWIFT code corresponds to the bank's actual country of operation.
Accessing Reliable SWIFT Code Information
In our digital age, while finding SWIFT codes has become easier, verifying their accuracy remains paramount. Most banks publish their SWIFT codes—including those for specific branches—on official websites, representing the most authoritative source. Third-party databases and applications also offer lookup services, though users should exercise caution and verify information through multiple channels when possible.
For international business transactions, additional considerations like exchange rates, transfer fees, and destination country regulations may apply. Proactive communication with financial institutions before initiating transfers can help prevent complications.
The Growing Importance of SWIFT Codes
As global financial transactions continue to expand, proficiency with SWIFT/BIC codes has transitioned from specialized knowledge to essential banking literacy. These standardized codes serve as vital communication tools in international commerce, enabling secure and efficient cross-border payments for individuals, small businesses, and multinational corporations alike.
Mastering SWIFT/BIC codes not only facilitates successful transactions but also builds confidence in international financial operations. In an increasingly connected global economy, this knowledge empowers users to navigate cross-border payments with greater assurance and precision.