In an era of rapid financial globalization, international fund transfers have become a daily necessity. As cross-border transactions accelerate, the demand for efficient and secure remittance solutions continues to grow. Among the critical components of this process, the correct use of SWIFT codes stands out as a fundamental requirement for seamless global banking operations.
Understanding SWIFT Codes
A SWIFT code, also known as a Bank Identifier Code (BIC), is a unique alphanumeric identifier assigned by the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) to financial institutions worldwide. This 8 to 11-character code serves as an international "passport" for money transfers, enabling banks to accurately identify recipients and ensure funds reach their intended destination.
The precision of SWIFT codes is paramount—any discrepancies in spelling or formatting may result in delayed transactions or misdirected funds. Thus, verifying the correct SWIFT code remains an essential step in cross-border payments.
MEGA International Commercial Bank Details
For transactions involving MEGA International Commercial Bank, the SWIFT code ICBCTWTP005 must be used. This code consists of 8 characters and contains vital information about the bank's identity and location. Below are the bank's key details:
- Bank Name: MEGA INTERNATIONAL COMMERCIAL BANK CO., LTD.
- City: Taipei
- Address: No. 233, Section 4, Zhongxiao East Road, Taipei
- Country: Taiwan
Structure of a SWIFT Code
A standard SWIFT code is divided into distinct segments:
- Bank Code (4 letters): Identifies the financial institution (e.g., ICBC for MEGA International Commercial Bank).
- Country Code (2 letters): Follows ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 standards (e.g., TW for Taiwan).
- Location Code (2 letters): Specifies the bank's city or region.
- Branch Code (3 letters, optional): Identifies a specific branch. If omitted, the code typically refers to the bank's headquarters.
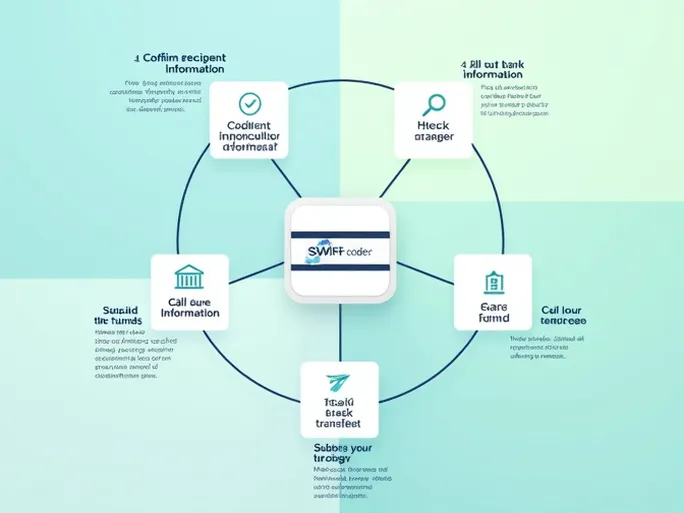
How to Use SWIFT Codes for International Transfers
To facilitate smooth cross-border transactions, follow these steps:
- Select a transfer method: Choose between bank wire transfers, electronic payments, or third-party services based on speed and cost considerations.
- Verify recipient details: Confirm the beneficiary's name, account number, and their bank's SWIFT code.
- Input bank information: Ensure the SWIFT code, bank name, and address match the recipient's records exactly.
- Review transaction details: Double-check all entered information before submission to prevent errors.
- Complete the transfer: Retain payment receipts for future reference and track the transaction until completion.
Key Considerations for Successful Transfers
To minimize risks in international remittances:
- Cross-verify the bank name and SWIFT code with official sources.
- Confirm whether a branch-specific code is required for the transaction.
- Validate the country code in the SWIFT identifier matches the recipient bank's location.
- Understand transfer fees and limits imposed by involved financial institutions.
- Maintain accurate contact information for both sender and recipient.
Preventing SWIFT Code Errors
To avoid common mistakes:
- Obtain SWIFT codes exclusively from bank websites or verified customer service channels.
- Maintain records of all transaction details for auditing purposes.
- Periodically confirm whether SWIFT codes have been updated due to banking reorganizations.
Conclusion
International fund transfers require meticulous attention to banking details, particularly SWIFT codes. By using MEGA International Commercial Bank's designated code (ICBCTWTP005) and adhering to established verification protocols, individuals and businesses can ensure efficient and secure global transactions. As financial systems continue to integrate worldwide, proper understanding of these mechanisms remains crucial for seamless cross-border payments.