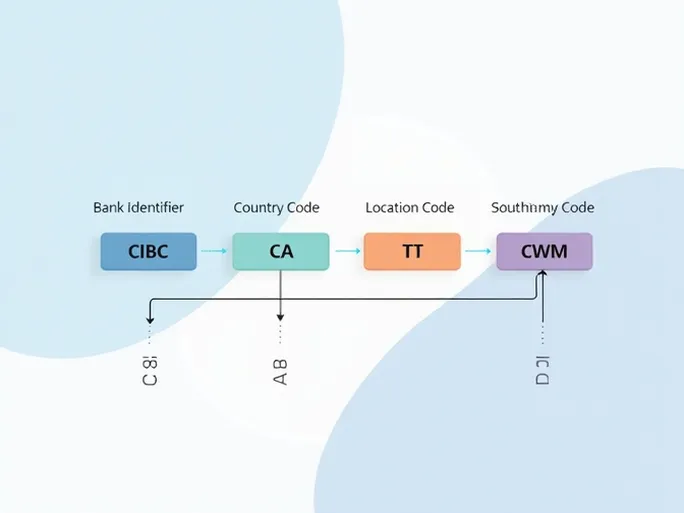
In international financial transactions, clear bank identification is paramount. Each financial institution operates with a unique SWIFT/BIC code that facilitates seamless confirmation and processing of cross-border payments. The Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (CIBC), for instance, uses the identifier CIBCCATTCWM—a sequence that not only verifies the bank's identity but also reveals specific branch information.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
These standardized codes consist of 8 to 11 characters that enable precise global identification of banks and their branches. The CIBC example demonstrates this structure:
- First 4 characters (CIBC): The bank's unique identifier
- Next 2 letters (CA): Country code (Canada)
- Following 2 characters (TT): Location indicator for the bank's headquarters
- Final 3 letters (CWM): Specific branch designation
When a code terminates with "XXX," this universally indicates the institution's primary office rather than a subsidiary branch.
Operational Advantages in Global Finance
This systematic coding framework delivers three critical benefits to international banking:
First, it eliminates ambiguity in payment routing, ensuring funds reach their intended destination. Second, the standardized format accelerates processing times compared to manual verification methods. Third, it reduces errors that previously led to delayed or misdirected transactions.
As cross-border commerce and investment continue expanding, understanding these identifiers becomes increasingly vital. Both corporations and individuals conducting international payments will find that accurate SWIFT/BIC information prevents transaction complications and safeguards fund transfers.
The financial industry's adoption of this universal system reflects its commitment to operational efficiency. What began as a solution for telegraphic transfers now underpins the infrastructure of modern global finance, demonstrating how standardized protocols can solve complex logistical challenges.