In modern financial transactions, the security and efficiency of cross-border payments represent critical concerns for both individual users and corporate clients, while remaining a key focus for financial institutions and regulators worldwide. Within this complex yet vital domain, the SWIFT/BIC code system serves as an international standard that ensures funds are transferred accurately and swiftly to designated banks and their branches.
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) provides a secure and efficient communication network for global financial institutions, with BIC (Bank Identifier Code) being its fundamental component. These globally unique codes, typically consisting of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters, identify specific banks and their geographic locations. For instance, LLOYDS BANK PLC's SWIFT/BIC code is LOYDGB21217. Understanding the structure, function, and application of these codes offers valuable insight into international financial transactions.
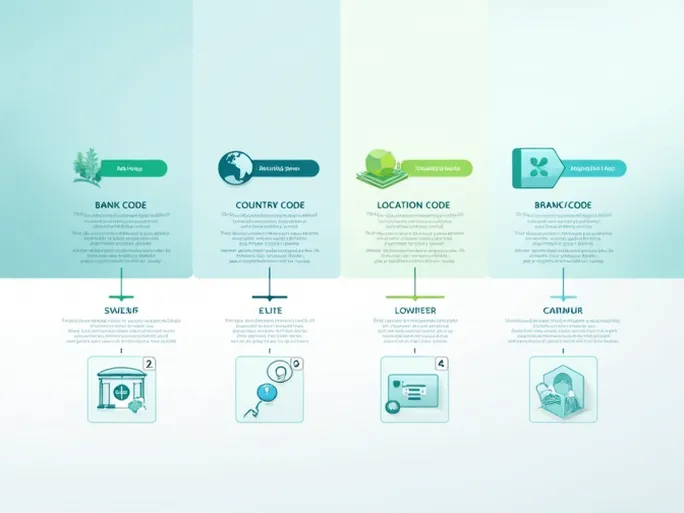
Anatomy of a SWIFT/BIC Code
The SWIFT/BIC code structure can be broken down into distinct components that reveal important information about the financial institution:
- Bank Code: The first four letters represent the bank's unique identifier (e.g., "LOYD" for LLOYDS BANK PLC).
- Country Code: The following two letters indicate the bank's country of operation ("GB" for United Kingdom).
- Location Code: The next two characters (numbers or letters) identify the bank's specific location ("21" in the LLOYDS example).
- Branch Code: The optional final three digits designate particular branches ("217" in this case), which proves especially important for international transfers.
The Critical Importance of SWIFT/BIC Codes
These standardized codes serve multiple essential functions in global finance:
First, they ensure transactional accuracy by precisely identifying recipient banks and branches, significantly reducing transfer errors. Second, they enhance efficiency by streamlining cross-border payments, which typically complete within a few business days. Third, they provide robust security measures that protect transaction integrity and minimize fraud risks during fund transfers.
Best Practices for SWIFT/BIC Code Usage
When initiating international transfers, users should adhere to these key verification steps:
- Confirm the recipient bank's exact legal name matches the SWIFT code
- Verify whether a specific branch code is required for the transaction
- Double-check the country designation in the code
- When necessary, validate the bank's physical address alongside its SWIFT code
Evolving Standards and Technological Advancements
Financial institutions periodically update their SWIFT/BIC codes due to mergers, system upgrades, or operational changes. Regular verification of code validity remains crucial for maintaining transaction security. Meanwhile, emerging technologies like blockchain present new possibilities for cross-border payments, though SWIFT maintains its dominant position in international finance. The integration of modern payment platforms with traditional banking systems continues to enhance transparency and user experience while meeting evolving regulatory requirements.
In today's rapidly globalizing economy, mastery of SWIFT/BIC code fundamentals empowers both individuals and businesses to navigate international finance with confidence, ensuring secure and efficient movement of funds across borders.