In today’s globalized financial landscape, cross-border transactions have become an essential part of daily life. At the heart of this process lies the SWIFT/BIC code, a standardized identifier that ensures secure and efficient international transfers. For instance, the SWIFT/BIC code for the Bank of Montreal (BMO) is BOFMCAM2NBB .
Understanding SWIFT/BIC Codes
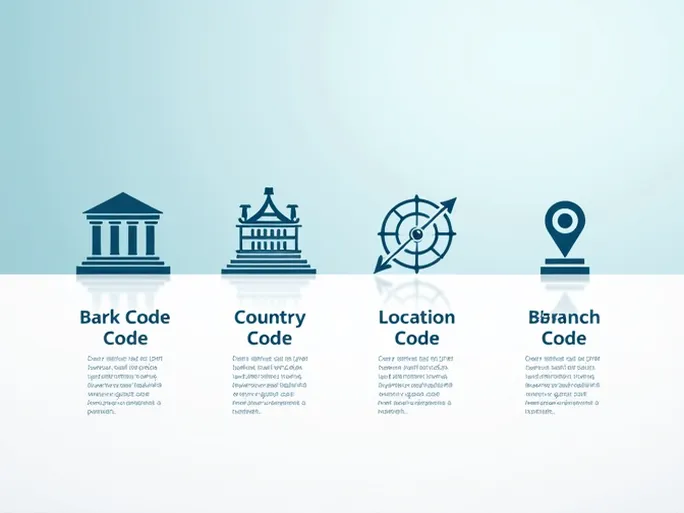
A SWIFT/BIC code typically consists of 8 to 11 characters, uniquely identifying a bank and its specific branch. The code is structured into four key components:
- Bank Code (BOFM) : Identifies the Bank of Montreal, distinguishing it from other financial institutions.
- Country Code (CA) : Specifies Canada as the bank’s home country, ensuring compliance with international transfer protocols.
- Location Code (M2) : Pinpoints the bank’s regional branch, adding geographical precision.
- Branch Code (NBB) : Optional details for identifying specific service outlets, further refining the transaction path.
Global Applications and Security
SWIFT codes are used worldwide to facilitate international wire transfers, reducing risks associated with cross-border payments. Verifying the accuracy of these codes is critical to ensuring timely and secure delivery of funds.
The Bank of Montreal has consistently prioritized customer security and service excellence. By maintaining up-to-date SWIFT/BIC information and refining its international network, BMO enhances the efficiency of cross-border banking for its clients.
Practical Considerations for Users
When initiating international transactions, customers should not only verify the recipient’s SWIFT/BIC code but also research transfer policies, fees, and processing times. This diligence minimizes costs and maximizes transaction success rates.
In summary, familiarity with SWIFT/BIC codes—such as BMO’s BOFMCAM2NBB —is fundamental to executing secure international transfers. Whether for personal or corporate use, accuracy in these details is paramount for seamless financial operations.