In today’s globalized era, international money transfers have become commonplace. Whether for purchasing goods and services or supporting family and friends abroad, accurate and timely fund transfers are critical. However, the process can be complex, particularly when selecting the correct banking details—such as SWIFT codes—which play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless transactions. This article explores the SWIFT code for NATIONAL COMMERCIAL BANK, including its structure, significance, and practical considerations.
Why SWIFT Codes Matter
A SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) code, also known as a Bank Identifier Code (BIC), is a standardized international code used to identify financial institutions globally. Comprising 8 to 11 characters, it uniquely specifies a bank’s name, country, city, and branch.
Providing the correct SWIFT code is mandatory for international transfers. An incorrect code may route funds to the wrong bank or halt the transaction entirely. Understanding the code’s structure minimizes risks and ensures funds reach their intended destination.
Decoding NATIONAL COMMERCIAL BANK’s SWIFT Code
Libya’s NATIONAL COMMERCIAL BANK, a historically significant financial institution, uses the SWIFT code LNCBLYLT050 . Its components are:
- LNCB : Bank identifier (NATIONAL COMMERCIAL BANK).
- LY : Country code (Libya).
- LT : Location code (Tripoli).
- 050 : Optional branch code (specific to a branch).
This code enables precise routing of funds. Verifying its accuracy is essential to avoid delays or losses.
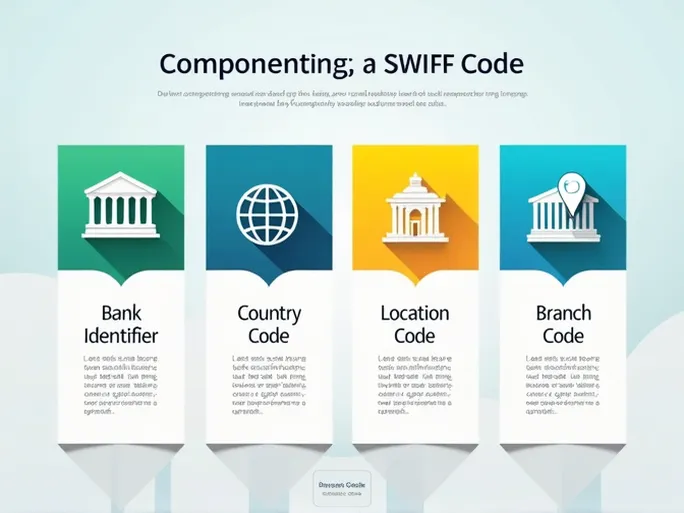
Anatomy of a SWIFT Code
SWIFT codes follow a logical structure:
- Bank Code (4 characters) : Identifies the bank (e.g., LNCB for NATIONAL COMMERCIAL BANK).
- Country Code (2 characters) : ISO-assigned country abbreviation (e.g., LY for Libya).
- Location Code (2 characters) : Specifies the city (e.g., LT for Tripoli).
- Branch Code (3 characters, optional) : Pinpoints a specific branch; omitted for head offices.
This systematic approach ensures funds are routed accurately across borders.
Ensuring SWIFT Code Accuracy
To prevent errors:
- Verify with the recipient : Confirm the code directly, especially for new or infrequent transactions.
- Use official sources : Rely on bank websites or customer service, not third-party platforms.
- Cross-reference databases : Consult SWIFT code directories provided by financial institutions.
Additional Considerations for Cross-Border Transfers
Beyond SWIFT codes, keep these factors in mind:
- Fees : International transfers often incur bank charges; clarify costs upfront.
- Exchange rates : Rates fluctuate; compare options to minimize losses.
- Processing time : Transfers typically take 3–5 business days; plan accordingly.
- Regulatory compliance : Adhere to local laws governing cross-border transactions.
- Documentation : Retain transaction records for future reference.
Mastering SWIFT codes and international transfer protocols empowers individuals and businesses to navigate global finance confidently. By prioritizing accuracy and diligence, you can ensure efficient, secure transactions—turning potential challenges into seamless financial exchanges.