In today's increasingly globalized world, cross-border money transfers have become routine for both individuals and businesses. However, the complexity of international transactions often causes confusion, particularly when moving funds between different countries and financial institutions. The SWIFT/BIC code plays a vital role in this process, ensuring funds reach their intended recipients quickly and accurately.
I. Fundamentals of SWIFT/BIC Codes
A SWIFT code (also known as BIC code) is a unique identifier assigned by the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) to identify financial institutions and their locations. This code typically consists of 8-11 characters that guarantee the security and precision of international payments.
The standard SWIFT code format comprises four components:
- Bank code (4 letters) : Usually an abbreviation of the financial institution's name.
- Country code (2 letters) : Indicates the institution's country, following ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 standards.
- Location code (2 letters/numbers) : Typically identifies the city or region.
- Branch code (3 letters/numbers, optional) : Specifies a particular branch.
This structured format enables financial institutions to communicate effectively worldwide while providing essential identification information.
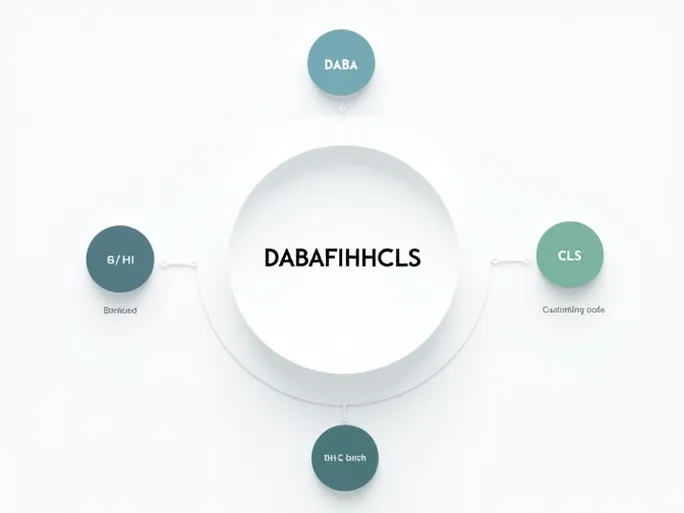
II. Decoding DABAFIHHCLS
Let's examine the specific components of the DABAFIHHCLS SWIFT/BIC code to understand its representation and functionality.
1. Bank Code (DABA)
The DABA component identifies Danske Bank A/S, one of Scandinavia's largest financial institutions. With operations across multiple countries, Danske Bank offers comprehensive financial services. This unique identifier ensures all transactions bearing this code relate specifically to Danske Bank.
2. Country Code (FI)
The FI country code designates Finland, allowing banking systems to quickly identify the transaction's destination country. Accurate country codes significantly reduce error potential during international transfers.
3. Location Code (HH)
The HH location code pinpoints the bank's position in Helsinki, Finland's capital and financial hub. Many international banks maintain primary offices in this city, making precise location identification crucial for efficient transactions.
4. Branch Code (CLS)
The CLS branch code specifies a particular Danske Bank branch in Helsinki. This level of detail helps identify specific services, operating hours, and contact information associated with that branch.
Collectively, DABAFIHHCLS serves as a unique identifier for Danske Bank's Finnish branch, facilitating secure and efficient international transactions.
III. The Role of DABAFIHHCLS in International Transfers
1. Enhanced Transaction Security
Using SWIFT codes like DABAFIHHCLS significantly improves transfer security. The SWIFT system's rigorous certification process ensures only legitimate financial institutions receive codes, substantially reducing fraud risks.
2. Precise Fund Routing
Accurate SWIFT code usage guarantees funds reach the intended Danske Bank branch in Finland. Errors could redirect payments to unrelated institutions, potentially causing financial losses and complex recovery processes.
3. Streamlined Procedures
Standardized identifiers like DABAFIHHCLS simplify international transfer documentation requirements. When financial institutions can quickly verify transaction participants, processing times decrease significantly—particularly valuable for time-sensitive transactions.
IV. Ensuring Proper Usage of DABAFIHHCLS
Correct application of the DABAFIHHCLS code is essential for risk-free international transfers. Consider these practical guidelines:
- Verify the SWIFT code through official bank resources before initiating transfers
- Understand the complete transfer process, including documentation requirements and processing timelines
- Maintain clear communication with recipients throughout the transfer process
V. The Future of DABAFIHHCLS and SWIFT Codes
Financial institutions continue adopting emerging technologies like blockchain to create more efficient, transparent transfer systems. While innovations may introduce alternative payment methods, SWIFT codes like DABAFIHHCLS will likely maintain fundamental roles in standardized international transactions.
VI. Conclusion
The DABAFIHHCLS SWIFT/BIC code provides critical identification for Danske Bank's Finnish operations, ensuring secure and efficient international transactions. Proper understanding and application of this and other SWIFT codes helps prevent errors and builds confidence in cross-border payments.
As global finance evolves with technological advancements, SWIFT codes will continue adapting while maintaining their essential function in international banking. For individuals and businesses navigating this complex landscape, mastering these identifiers remains fundamental to successful global financial operations.