In today's highly interconnected global economy, the fluidity of capital has become increasingly critical. Whether for personal cross-border remittances or commercial transactions between businesses, ensuring funds reach their destination swiftly and accurately is a universal priority. Within this complex financial ecosystem, SWIFT/BIC codes serve as an indispensable tool—not merely as a combination of letters and numbers but as a vital bridge facilitating secure and efficient communication between financial institutions worldwide.
Understanding SWIFT/BIC Codes
SWIFT, an acronym for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, operates one of the largest payment networks globally. Each financial institution participating in the SWIFT network is assigned a unique SWIFT/BIC code, which enables banks to identify and process transactions, including international wire transfers. This standardized coding system has effectively replaced outdated methods like fax or manual processing, significantly enhancing both the security and efficiency of cross-border payments.
Decoding the Structure of SWIFT/BIC Codes
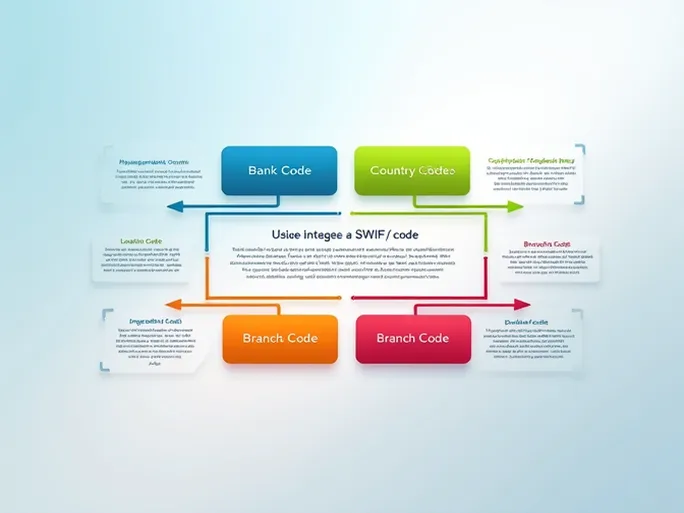
A SWIFT/BIC code typically consists of 8 to 11 characters. For example, the Finnish bank NORDEA BANK ABP uses the code NDEAFIHHIPL , which can be broken down as follows:
- Bank Code (NDEA) : The first four letters represent the bank's abbreviated name, allowing immediate recognition by other financial institutions.
- Country Code (FI) : The next two letters denote the country where the bank is registered—in this case, Finland.
- Location Code (HH) : These two characters specify the bank's headquarters or primary operational center. The final three digits (e.g., IPL) may indicate a specific branch, while "XXX" typically refers to the institution's head office.
Key Considerations for International Transfers
To minimize errors and ensure seamless transactions, individuals and businesses must verify the following details before initiating an international transfer:
- Bank Name Accuracy : Confirm that the recipient bank's name matches the details provided in the SWIFT/BIC code.
- Branch Specificity : If using a branch-specific code, validate that it corresponds to the recipient's account location.
- Country Consistency : Ensure the country code aligns with the recipient bank's actual jurisdiction to avoid misdirected payments.
Optimizing Cross-Border Payments
Beyond understanding SWIFT codes, selecting an efficient payment service provider can further enhance the speed and cost-effectiveness of international transfers. Competitive exchange rates, transparent fee structures, and rapid processing times are among the factors that distinguish leading remittance platforms.
Additional strategies to optimize international transactions include:
- Monitoring Exchange Rates : Tracking real-time currency fluctuations can help identify favorable transfer windows.
- Utilizing Rate Alerts : Automated notifications for target exchange rates enable timely execution of transfers.
- Comparing Transfer Methods : Evaluating the trade-offs between bank transfers, digital wallets, and other payment channels ensures optimal routing based on urgency and cost considerations.
Mastering these elements empowers individuals and businesses to navigate the complexities of global finance with confidence, ensuring each transaction is executed with precision and efficiency.

