The complexity of SWIFT/BIC codes often leaves many perplexed when initiating international wire transfers. However, understanding these banking identifiers is simpler than it appears. Comprising 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters, SWIFT/BIC codes precisely identify financial institutions and their specific branches worldwide.
Decoding the Structure
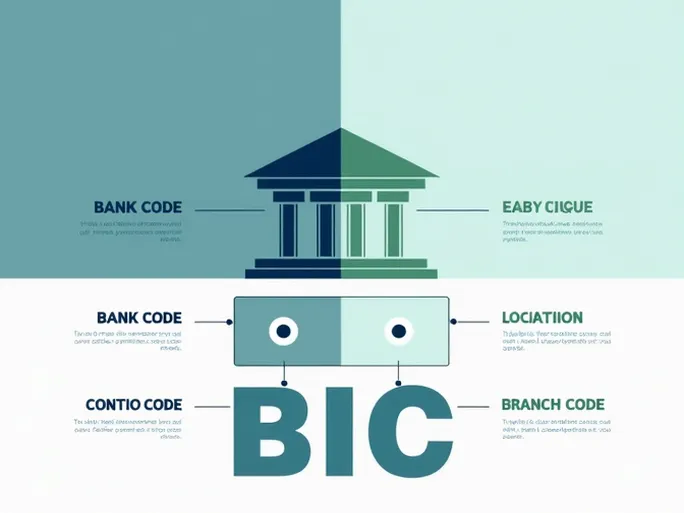
A standard SWIFT/BIC code consists of four distinct components:
- Bank Code (4 characters) : Identifies the financial institution (e.g., "BCIT" for Intesa Sanpaolo S.p.A.).
- Country Code (2 characters) : Indicates the bank's registered country (e.g., "IT" for Italy).
- Location Code (2 characters) : Specifies the bank's headquarters city.
- Branch Code (3 characters) : Identifies specific branches ("XXX" denotes the head office).
Essential Verification Steps
Accurate SWIFT code usage is critical for successful international transactions. These precautions can prevent processing delays and potential financial losses:
- Bank Name Verification : Ensure the recipient bank's legal name matches exactly with the registered SWIFT code information.
- Branch Specificity : When using a branch-specific code, confirm its alignment with the recipient's account location.
- Country Consistency : Verify that the SWIFT code corresponds to the correct destination country, particularly for multinational banks.
Financial experts recommend direct confirmation with recipients before initiating transfers. Proper understanding of SWIFT/BIC protocols not only safeguards funds but also optimizes transaction efficiency. Mastering these banking identifiers empowers individuals and businesses to conduct international payments with confidence.