In international banking, the SWIFT/BIC code serves as an essential identifier that ensures smooth cross-border transactions. Many have experienced the frustration of delayed transfers, often due to incorrect or incomplete banking information. Understanding how to properly use these codes is crucial for anyone involved in international money transfers.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
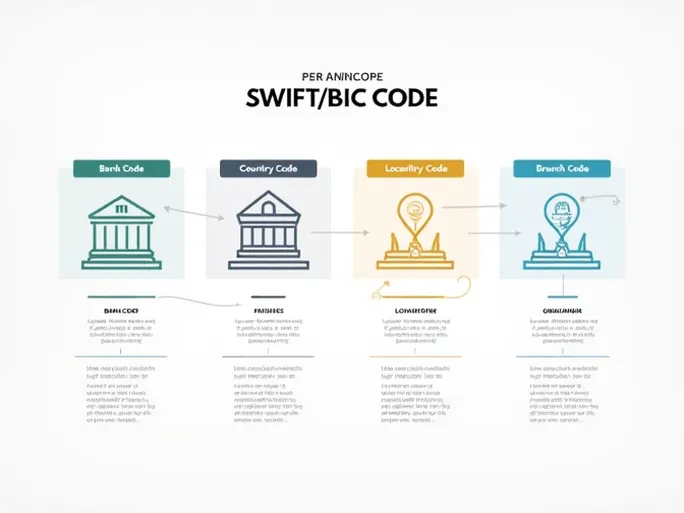
A SWIFT/BIC code consists of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters, each segment carrying specific information. Taking NATIONAL BANK LIMITED as an example with its code NBLBBDDH006, we can analyze the components:
- Bank Code (NBLB): The first four characters identify the financial institution (NATIONAL BANK LIMITED).
- Country Code (BD): The following two letters indicate the bank's country of origin (Bangladesh).
- Location Code (DH): These two characters specify the bank's headquarters city or region (Dhaka).
- Branch Code (006): The final three digits pinpoint the exact branch location.
Important Considerations for International Transfers
When a SWIFT code ends with "XXX," this typically refers to a bank's head office rather than a specific branch. The accuracy of this information directly impacts transaction success - even minor errors can cause significant delays or failed transfers.
Financial institutions and individuals must verify both the recipient bank's name and corresponding SWIFT/BIC code before initiating any international payment. This simple verification step can prevent unnecessary complications and ensure funds reach their intended destination promptly.
By understanding the structure and significance of SWIFT/BIC codes like that of NATIONAL BANK LIMITED, individuals and businesses can conduct international financial transactions with greater confidence and efficiency.