When making international wire transfers, even a minor error in the SWIFT/BIC code can lead to delays or complications—especially for high-value transactions. One such critical code is NOSCCATTCT2 , used by The Bank of Nova Scotia in Canada. Understanding its structure and verification steps can help streamline cross-border payments.
Decoding SWIFT/BIC: What Each Segment Means
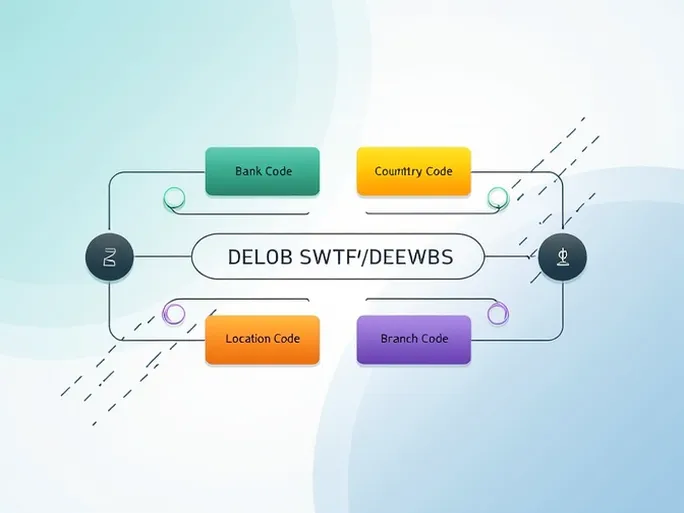
A SWIFT/BIC code is an 8–11 character identifier that pinpoints a specific bank and branch globally. Here’s how NOSCCATTCT2 breaks down:
- Bank Code (NOSC) : The first four letters represent The Bank of Nova Scotia.
- Country Code (CA) : The next two characters indicate Canada as the bank’s home country.
- Location Code (TT) : These two digits or letters specify the bank’s headquarters.
- Branch Code (CT2) : The final three characters identify a specific branch. A code ending with "XXX" typically denotes the bank’s head office.
This standardized system ensures precise routing of funds, minimizing errors in global transactions.
Key Steps to Avoid Transfer Issues
To prevent delays or misdirected payments, adhere to these guidelines:
- Verify the Bank Name : Confirm that the recipient’s bank name matches the SWIFT/BIC code.
- Check the Branch : If using a branch-specific code, ensure it aligns with the recipient’s account details.
- Confirm the Country : Cross-check that the SWIFT code corresponds to the correct country where the recipient’s bank operates.
Conclusion: Accuracy Is Paramount
International wire transfers demand meticulous attention to detail. Verifying SWIFT/BIC codes—including the bank, branch, and country—helps safeguard against costly mistakes. Before initiating any transfer, double-check all details with the recipient and consult your bank for clarification if needed. With the right precautions, global transactions can be executed seamlessly and securely.