In today's rapidly evolving digital banking landscape, accurately identifying specific financial institutions for international money transfers remains crucial. The SWIFT/BIC code system was specifically designed to address this need, serving as a universal identifier for banks and their branches worldwide.
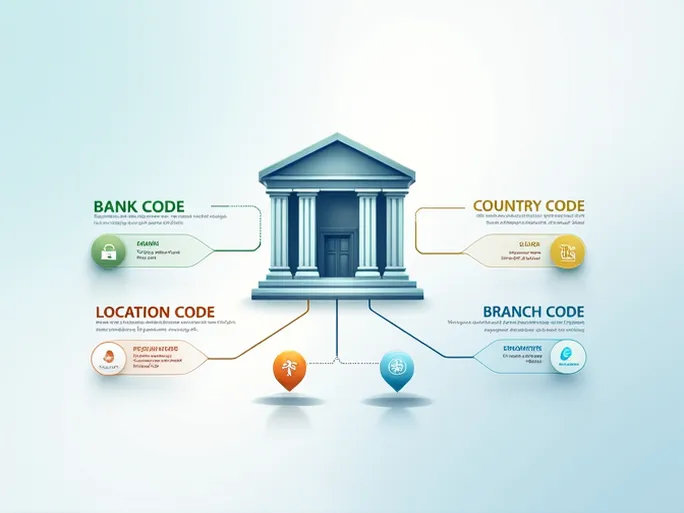
Each SWIFT/BIC code consists of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters that convey specific information about the financial institution:
- Bank Code (4 characters): The initial four letters identify the specific bank (e.g., HBTS for Bank of Scotland PLC).
- Country Code (2 characters): The following two letters indicate the bank's home country (GB for United Kingdom).
- Location Code (2 characters): These characters specify the bank's headquarters location within its international network.
- Branch Code (3 characters, optional): The final three digits identify specific branches, with 'XXX' typically representing the main office.
The Critical Importance of Accuracy
Precise use of SWIFT/BIC codes proves essential for ensuring timely and successful international transfers. Incorrect codes may result in significant delays or even failed transactions. Financial experts strongly recommend verifying both the bank name and recipient details before initiating any transfer.
SWIFT transfers generally offer competitive advantages in terms of processing fees, making them an attractive option for cost-conscious clients. Most transactions clear within the same business day, providing efficient movement of funds between accounts. This combination of affordability and speed makes understanding the system particularly valuable for time-sensitive transfers.
Financial institutions continue to refine their international transfer processes, with accurate SWIFT/BIC code usage remaining a cornerstone of successful cross-border banking operations. As digital banking evolves, these standardized identifiers maintain their role as critical components in global financial infrastructure.