When making international money transfers, ensuring funds reach the correct recipient account requires precise banking information. Each cross-border transaction relies on a crucial identifier: the SWIFT/BIC code. The case of Denmark's central bank, Danmarks Nationalbank, with its SWIFT code DKNBDKKKDEP, offers valuable insights into how these codes function.
The Anatomy of a SWIFT Code
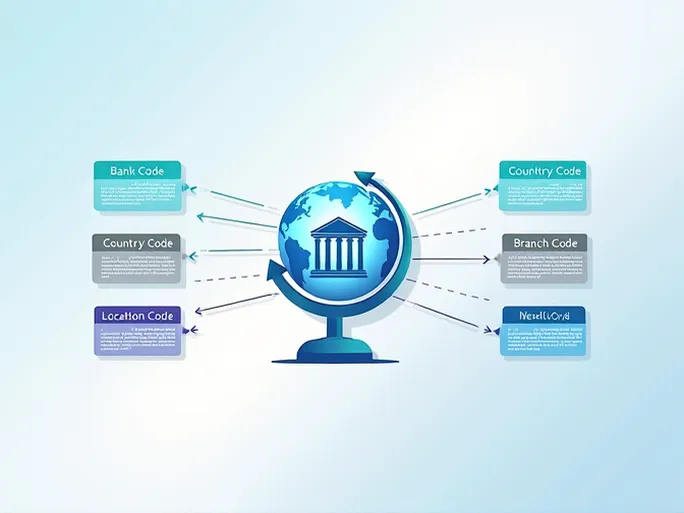
SWIFT codes serve as unique identifiers for financial institutions in international transactions. These 8-11 character combinations act like digital addresses, ensuring funds are routed correctly across global banking networks.
The structure of Danmarks Nationalbank's code DKNBDKKKDEP reveals how these identifiers work:
- DKNB identifies the specific bank (Danmarks Nationalbank)
- DK designates the country (Denmark)
- KK indicates the bank's location
- DEP specifies the branch (if applicable)
Why SWIFT Codes Matter
Accurate SWIFT information prevents transaction delays and potential financial losses. Errors in these codes may result in funds being misdirected or held in limbo while financial institutions investigate.
For businesses and individuals conducting international transactions, verifying the correct SWIFT code with recipient banks remains essential. This verification step becomes particularly crucial when dealing with institutions that maintain multiple branches or operate under similar names in different countries.
Financial institutions periodically update their SWIFT information, making reconfirmation before each significant transfer a prudent practice. While central banks like Danmarks Nationalbank typically maintain consistent codes, commercial banks may implement changes due to mergers, acquisitions, or operational restructuring.