In today's increasingly globalized world, international money transfers have become essential for both individuals and businesses. Whether for commercial purposes, family support, or other personal needs, the convenience and security of cross-border financial transactions have grown in importance. However, as financial globalization deepens, the complexity of international transfers has also increased. Understanding and utilizing relevant banking codes, such as SWIFT codes, has therefore become crucial.
The Origin and Function of SWIFT Codes
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) was established in 1973 and has since become the primary communication platform for international bank transfers. A SWIFT code is a standardized data format that enables secure and efficient communication between financial institutions. Each SWIFT code consists of 8 or 11 characters containing key information about the bank's identity and geographical location. These codes not only help senders identify recipient banks but also facilitate the smooth transfer of funds between different financial institutions.
The Role of NEDERLANDSCHE BANK (DE) N.V.
As the central bank of the Netherlands, NEDERLANDSCHE BANK plays a vital role in the country's economy. It is responsible for monetary policy and financial stability while supporting the security and efficiency of the banking system. The SWIFT code ECMSNL2A XXX specifically represents NEDERLANDSCHE BANK, ensuring that customers' funds are accurately transferred to designated accounts.
Structure of SWIFT Codes
SWIFT codes are typically composed of four distinct parts:
- First four characters (bank code): For example, ECMS identifies NEDERLANDSCHE BANK.
- Next two characters (country code): NL represents the Netherlands.
- Following two characters (location code): 2A indicates the bank's location in Amsterdam.
- Final three characters (optional branch code): When absent, XXX is used to denote the bank's headquarters.
This structure allows for precise identification of banks and specific branches worldwide, facilitating efficient fund transfers.
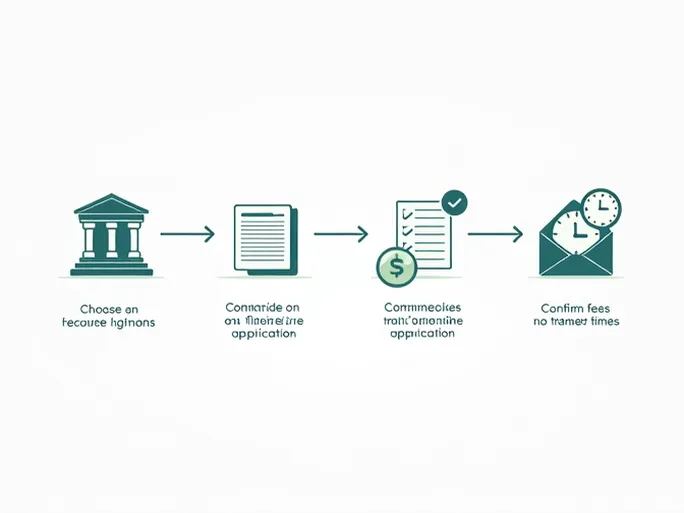
The International Transfer Process
International money transfers generally follow these key steps:
- Selecting a reliable financial institution for the transfer
- Providing complete recipient bank details including SWIFT code, account number, and bank name
- Completing the transfer application carefully to ensure all information is accurate
- Verifying network status and understanding applicable fees and processing times
- Tracking the transfer status through the financial institution's services
Verifying SWIFT Codes
In international transfers, SWIFT codes are critical for ensuring funds reach their intended destination. Even minor errors in these alphanumeric codes can cause transfer failures. Incorrect SWIFT codes may result in funds being sent to wrong accounts or becoming frozen and unrecoverable in some cases.
Additional Considerations for Cross-Border Transfers
Beyond SWIFT codes, several other factors influence international money transfers:
Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact the final amount received. Monitoring market rates and choosing optimal times for transfers can yield better financial outcomes.
Fee Structures: Different financial institutions have varying fee policies for international transfers. Some charge fixed fees while others apply percentage-based charges or additional intermediary bank fees. Understanding these costs beforehand helps avoid unexpected deductions.
Processing Times: Transfer durations vary by institution and payment method. While most standard transfers complete within 1-5 business days, factors like intermediary banks and holidays may extend this timeframe.
Modern Transfer Solutions
Traditional bank transfers are increasingly being supplemented by financial technology platforms that offer faster, more secure, and cost-effective alternatives. These services typically provide competitive exchange rates and lower fees compared to conventional banking options.
The process through these modern platforms generally involves:
- Account creation and identity verification
- Inputting recipient details including SWIFT codes
- Confirming transfer amounts and reviewing applicable rates and fees
- Submitting and tracking transfer requests
Many of these services also offer extended customer support to assist users throughout the transfer process.
International money transfers present complex challenges where accurate banking information, reasonable fee structures, and transparent processing times all significantly impact transaction success. Proper understanding of transfer mechanisms and careful attention to detail ensure funds reach their intended destinations securely and efficiently.