In international money transfers, SWIFT/BIC codes serve as crucial tools to ensure funds reach their destination accurately and promptly. These unique identifiers, typically consisting of 8 to 11 characters, contain specific information about financial institutions worldwide.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
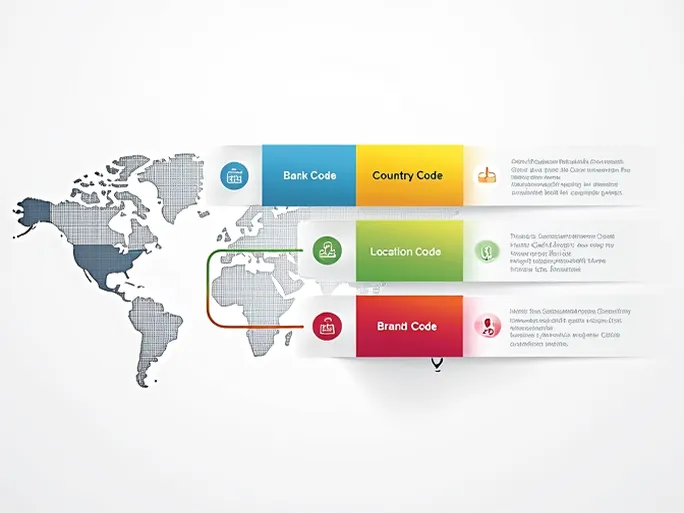
Taking SKANDINAVISKA ENSKILDA BANKEN AB (SEB) as an example, we can examine how these codes function. A typical SWIFT/BIC code like ESSESESLS breaks down into distinct components:
- Bank Code (ESSE) - Identifies the specific financial institution
- Country Code (SE) - Indicates Sweden as the bank's location
- Location Code (SS) - Specifies the bank's headquarters
- Branch Code (SLS) - Pinpoints a particular branch (or 'XXX' for headquarters)
Critical Verification Steps
Accuracy in using SWIFT codes cannot be overstated. Even minor errors can result in delayed transactions or funds being sent to incorrect accounts. Before initiating any international transfer, verify these essential elements:
- Confirm the bank name matches the recipient's financial institution exactly
- When using branch-specific codes, ensure the branch corresponds to the recipient's account
- Verify the country code aligns with the recipient bank's location
Proper understanding of SWIFT/BIC code structure and careful verification of transaction details provide the foundation for secure international banking. By following these protocols, individuals and businesses can conduct cross-border transactions with confidence, ensuring smooth and trouble-free financial operations.

