In today's increasingly interconnected financial world, SWIFT/BIC codes serve as critical identifiers for international money transfers. As digital technology and globalization continue to advance, cross-border transactions have become commonplace, making accurate and secure payment methods more important than ever.
These standardized codes, consisting of 8 to 11 characters, enable financial institutions to quickly identify recipient banks worldwide. By precisely directing funds to specific banks and their branches, SWIFT/BIC codes ensure both security and accuracy in global money transfers while offering users significant convenience.
The Origins and Evolution of SWIFT/BIC Codes
Understanding the function of SWIFT/BIC codes requires examining their history. SWIFT, an acronym for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, was established in 1973 to provide secure, reliable, and efficient communication services between banks globally.
As international trade expanded dramatically, traditional payment methods struggled to keep pace with growing transaction volumes. SWIFT emerged as the solution, offering a standardized approach to cross-border fund transfers. The SWIFT/BIC code serves as a unique identifier within this system, allowing financial institutions to accurately identify transaction recipients with international precision.
Decoding the Structure of SWIFT/BIC Codes
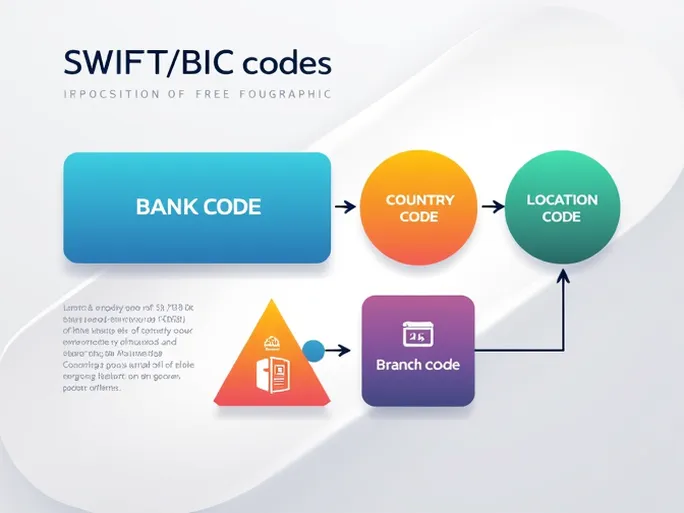
Consider the example of BANCOLOMBIA S.A.'s SWIFT/BIC code: "COLOCOBMCTG". This alphanumeric sequence contains distinct sections conveying specific information:
- Bank Code (COLO): The first four letters identify the specific financial institution. In this case, "COLO" represents BANCOLOMBIA S.A.
- Country Code (CO): The subsequent two letters indicate the bank's home country, with "CO" signifying Colombia.
- Location Code (BM): The next two characters specify the bank's city or primary location, crucial for understanding regional transaction rules and fee structures.
- Branch Code (CTG): The optional final three characters pinpoint a specific branch, ensuring funds reach the exact intended account within large banking networks.
In our example, "COLOCOBM" identifies BANCOLOMBIA's headquarters, while "CTG" directs funds to a particular branch. This structured approach significantly reduces transfer errors, safeguarding financial transactions.
Critical Considerations When Using SWIFT/BIC Codes
While SWIFT/BIC codes simplify international transfers, users should remain mindful of several key factors:
- Bank Verification: Always confirm that the recipient bank name matches the account details. Incorrect codes may route funds to unintended institutions, causing delays.
- Branch Accuracy: When using branch-specific codes, verify the exact branch location matches the recipient's information. This proves particularly important for large banks with numerous branches.
- Country Confirmation: Ensure the SWIFT code corresponds to the correct destination country. Even minor discrepancies in country codes can prevent successful transfers.
The Advantages of SWIFT/BIC Codes
SWIFT/BIC codes offer numerous benefits for international banking:
The standardized format streamlines cross-border payments by eliminating manual verification steps. This system dramatically reduces transaction errors and accelerates processing times. With near-universal participation in the SWIFT network, users enjoy exceptional flexibility in global money movement.
Perhaps most importantly, SWIFT's robust security protocols ensure encrypted data transmission, significantly minimizing interception risks during international transfers.
Optimizing International Money Transfers
When selecting transfer services, modern digital platforms often provide superior alternatives to traditional banks. Key advantages include:
- Competitive Exchange Rates: Digital services frequently offer more favorable currency conversion rates than conventional banks.
- Transparent Pricing: Upfront disclosure of all fees prevents unexpected charges and promotes financial clarity.
- Expedited Processing: Many digital transfers complete within the same business day, offering significant time savings.
Conclusion
As global economic activity intensifies, SWIFT/BIC codes remain indispensable tools for international finance. For both individuals and businesses, mastering these identifiers ensures secure, accurate fund transfers while providing greater flexibility in global transactions.
In our rapidly evolving financial landscape, meticulous attention to these details helps navigate the complexities of international payments, ensuring smooth participation in the global economy.