In an increasingly interconnected global economy, cross-border payments have become a routine financial activity for individuals and businesses alike. Yet, how many truly understand the importance of correctly using SWIFT/BIC codes? This article explores the SOGEFRPPACH SWIFT/BIC code and its pivotal role in international money transfers.
SOGEFRPPACH: The Global Identifier for Société Générale
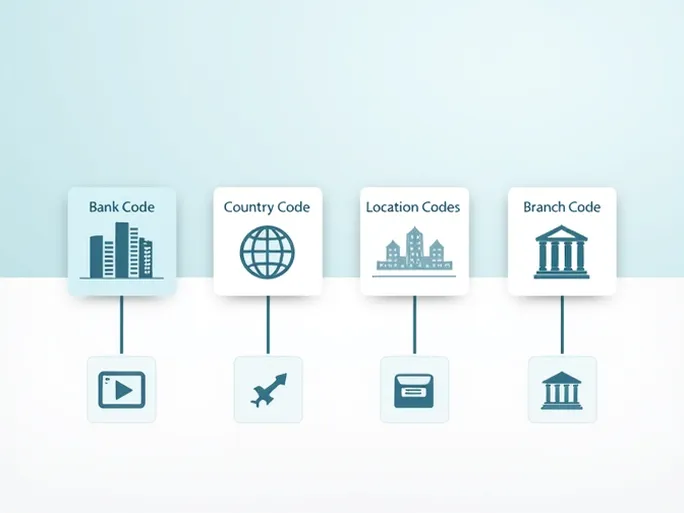
SOGEFRPPACH is the SWIFT/BIC code for Société Générale, a major French bank headquartered in Paris. This alphanumeric sequence serves as a unique identifier, with each segment conveying specific information:
- Bank Code (SOGE) : Identifies Société Générale as the financial institution.
- Country Code (FR) : Denotes France as the bank's location.
- Location Code (PP) : Points to the bank's primary office.
- Branch Code (ACH) : Specifies the particular branch (in this case, the ACH department).
When to Use SOGEFRPPACH
The correct SWIFT code is essential when transferring funds to Société Générale. Whether for personal remittances or commercial transactions, SOGEFRPPACH acts as the secure gateway to the bank. Verifying this code before initiating any transfer is crucial to prevent delays or potential loss of funds.
A Practical Example: GBP to EUR Transfer
Consider transferring £10,000 to a Société Générale account. At current exchange rates, the recipient would receive approximately €11,374. Using SOGEFRPPACH ensures this transaction typically processes within 24 hours, demonstrating how SWIFT codes facilitate efficient cross-border payments.
Understanding SWIFT/BIC Code Structure
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) established this standardized system in 1973 to secure international financial messaging. A typical SWIFT/BIC code contains 8-11 characters:
- Bank Code (4 letters) : Unique to each financial institution
- Country Code (2 letters) : Based on ISO 3166 standards
- Location Code (2 characters) : Identifies the bank's city
- Branch Code (3 characters, optional) : Specifies particular departments
The Impact of SWIFT Codes on Transactions
Incorrect SWIFT codes can cause significant issues:
- Payment delays of several days
- Potential loss of funds
- Additional fees for retrieval or correction
Additional Considerations for International Transfers
Beyond accurate SWIFT codes, successful transfers require attention to:
- Exchange Rates : Compare rates across providers
- Fees : Understand all applicable charges
- Processing Times : Account for holidays and weekends
Choosing Reliable Financial Institutions
When selecting a service provider for international transfers, consider:
- Regulatory compliance and reputation
- Security measures and encryption standards
- Transparency in fees and terms
The Future of Cross-Border Payments
While SWIFT/BIC codes remain the current standard, emerging technologies like blockchain may transform international payments. However, these codes will likely maintain their relevance in the near future.
Final Reminder
Always verify SWIFT codes with your bank before initiating transfers. For Société Générale transactions, ensuring you use SOGEFRPPACH when appropriate safeguards your funds and streamlines the transfer process.