In today's rapidly evolving global financial markets, the demand for international bank transfers continues to grow exponentially. As this demand increases, the importance of SWIFT/BIC codes in facilitating secure and efficient cross-border transactions becomes ever more apparent. Far from being just a random combination of letters and numbers, these codes serve as the backbone for accurate global financial communication.
Understanding the structure and practical application of the SWIFT/BIC system proves invaluable for both individuals and businesses engaged in international money transfers. To illustrate this system in action, we'll examine BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA as a case study, analyzing its SWIFT/BIC code structure and highlighting crucial considerations for successful transactions.
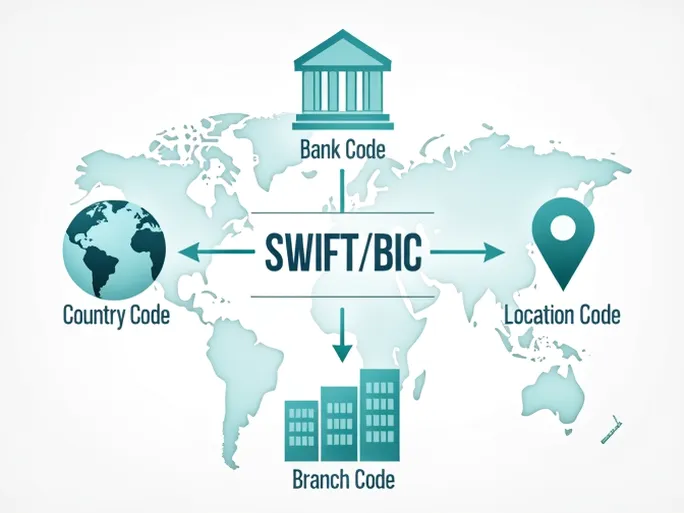
The Fundamental Structure of SWIFT/BIC Codes
A SWIFT/BIC code typically consists of 8 to 11 characters that uniquely identify financial institutions worldwide. Taking BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA's code MAOISMSM006 as an example, we can break it down into distinct components:
1. Bank Code (MAOI)
The first four letters specifically identify BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA, serving as a unique fingerprint that distinguishes it from other financial institutions and prevents processing errors.
2. Country Code (SM)
The subsequent two-letter code indicates the bank's registered country - in this case, San Marino. This geographical identifier plays a pivotal role in routing international transfers correctly.
3. Location Code (SM)
Following the country code, another two-letter segment pinpoints the bank's headquarters location within its home country, particularly important for domestic clearing operations.
4. Branch Code (006)
The final three digits (when present) identify specific branches. The 006 in our example refers to a particular branch of BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA. When a code ends with "XXX," it typically indicates the institution's head office rather than a specific branch.
This systematic breakdown demonstrates how the SWIFT/BIC framework ensures precision and security in global financial communications, forming an invisible infrastructure that supports international commerce.
Decoding BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA's SWIFT/BIC Information
Examining BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA's complete details provides concrete insight into how SWIFT/BIC codes translate into real-world banking information:
- SWIFT/BIC Code: MAOISMSM006
- Bank Name: BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA
- Address: VIA STRADA DELLA CROCE, 39
- City: FAETANO
This transparency exemplifies modern international banking's commitment to clear, accessible financial information - a cornerstone of global economic integration.
Essential Considerations for Using SWIFT Codes
When initiating international transfers, attention to detail with SWIFT codes can mean the difference between seamless transactions and costly errors. Key verification steps include:
- Bank Name Verification: Confirm the recipient bank's exact legal name matches your records to prevent transfer rejections.
- Branch Specifics: When using branch-specific codes, verify that the designated branch actually services the recipient's account.
- Country Code Accuracy: Double-check the two-letter country code to avoid misdirecting funds to wrong jurisdictions.
- Amount and Currency Confirmation: Scrutinize transfer amounts and currency selections, as these directly impact exchange rates and fees.
- Recipient Communication: Maintain clear dialogue with recipients to confirm all banking details and special requirements before initiating transfers.
Security Implications of the SWIFT/BIC System
Beyond its routing function, the SWIFT network incorporates robust security measures that safeguard international transactions. Participating financial institutions must adhere to stringent security protocols including:
- Advanced encryption standards for all transmitted data
- Multi-factor authentication mechanisms
- Comprehensive auditing and compliance requirements
These collective measures create a secure environment for trillions of dollars in daily cross-border transactions, maintaining confidence in the global financial system.
The Future of International Money Transfers
As digital transformation accelerates across financial services, SWIFT continues evolving to meet new challenges. Recent innovations include:
- Implementation of ISO 20022 standards for richer payment data
- Development of real-time cross-border payment capabilities
- Enhanced APIs for seamless integration with banking systems
These advancements promise to further streamline international transactions while maintaining the reliability that has made SWIFT the global standard for bank communications.
In our interconnected global economy, proficiency with SWIFT/BIC codes has become essential financial literacy. Whether transferring funds for personal reasons or conducting multinational business transactions, understanding this system helps navigate the complexities of international banking with confidence. By paying careful attention to code details and following verification best practices, individuals and organizations can ensure their cross-border transfers proceed smoothly and securely.