In today's globalized world, international money transfers have become commonplace. Yet many are unaware that a correct SWIFT/BIC code is crucial for ensuring smooth transactions. These alphanumeric codes, typically 8 to 11 characters long, serve as unique identifiers for banks and their branches worldwide.
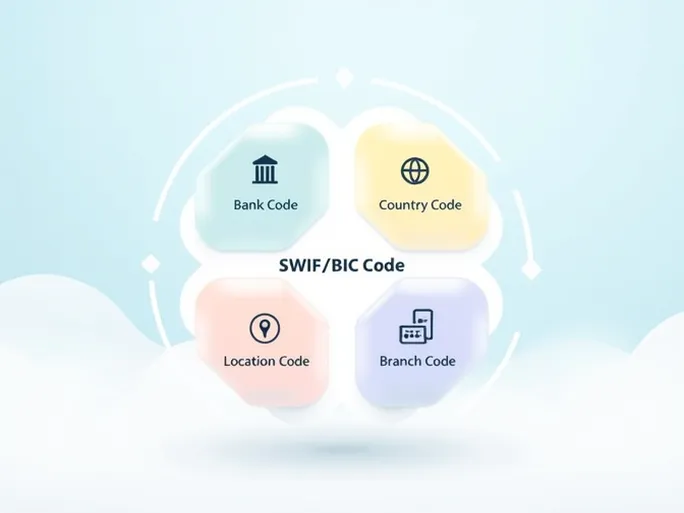
Consider the example of BANCA DI SAN MARINO SPA. A SWIFT/BIC code breaks down into four distinct components:
- Bank Code (MAOI): The first four letters identify the specific financial institution.
- Country Code (SM): Two letters denoting the bank's home country (in this case, San Marino).
- Location Code: Two characters indicating the bank's headquarters location.
- Branch Code (001): Three digits specifying a particular branch. A terminal "XXX" signifies the bank's head office.
Ensuring Accurate Transfers
The consequences of incorrect SWIFT information can range from processing delays to failed transactions. These verification steps can prevent such issues:
- Bank Name Verification: Cross-check that the financial institution name matches the recipient's bank exactly.
- Branch Specificity: When using a branch-specific code, confirm it corresponds with the recipient's actual branch location.
- Country Validation: Verify the country code aligns with the destination bank's physical location, as multinational banks operate across borders.
Understanding SWIFT/BIC code structure and application remains fundamental for international banking. This knowledge helps individuals and businesses navigate cross-border payments efficiently while minimizing potential complications.

