In today's interconnected global financial system, international money transfers serve as vital conduits for economic integration. Beyond simple fund transfers, these transactions represent economic and cultural bridges between nations. From business transactions to personal remittances, understanding the proper use of SWIFT/BIC codes has become essential for ensuring secure financial transfers.
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) provides a global messaging network that enables financial institutions to send and receive information about transactions in a secure, standardized environment. The system's importance is exemplified by institutions like Republic Bank Limited, which uses the SWIFT/BIC code RBNKTTPAXXX for international transactions.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC System
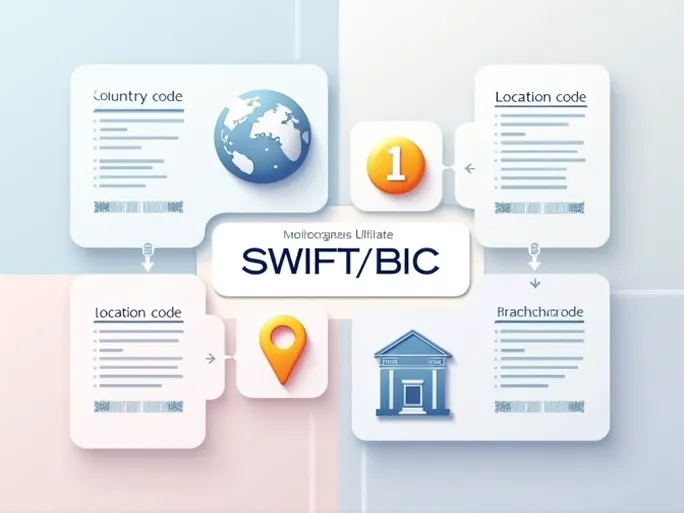
SWIFT/BIC codes follow a precise structure rather than being randomly generated. These 8-11 character codes contain specific information:
- Bank Code: The first four characters (e.g., RBNK for Republic Bank Limited) identify the specific financial institution.
- Country Code: The next two characters (TT for Trinidad and Tobago) specify the bank's location.
- Location Code: The following two characters (PA) identify the bank's specific geographic location.
- Branch Code: The final three characters (XXX) designate a particular branch, with XXX typically representing the bank's headquarters.
Republic Bank Limited: A Case Study
The SWIFT code RBNKTTPA directs transactions to Republic Bank Limited's headquarters in Trinidad and Tobago. Key details include:
- SWIFT Code: RBNKTTPA
- Branch Code: XXX
- Full Bank Name: Republic Bank Limited
- Address: Foreign Exchange CTR
- City: Port of Spain
Ensuring Accurate International Transfers
Verification of SWIFT code details is crucial before initiating any international transfer. Key verification steps include:
Bank Name Confirmation: Cross-check the recipient's bank name with official sources to avoid confusion between similarly named institutions.
Branch Verification: Confirm that the SWIFT code matches the recipient's specific branch, as different branches may have distinct codes.
Country Validation: Ensure the country code in the SWIFT/BIC corresponds to the intended destination country.
Optimizing International Money Transfers
International transfers often involve various fees and exchange rate considerations. Several factors can influence the total cost:
Competitive Exchange Rates: Some platforms offer more favorable exchange rates compared to traditional banks, potentially saving significant amounts on large transfers.
Transparent Fee Structures: Clear disclosure of all applicable fees before transaction confirmation helps prevent unexpected charges.
Transfer Speed: Processing times can vary significantly between providers, with some offering same-day completion for urgent transactions.
Common Challenges in International Transfers
Despite the efficiency of modern financial networks, international transfers can encounter several issues:
Transfer Delays: These may occur due to incorrect information, processing backlogs, or time zone differences between financial institutions.
Exchange Rate Fluctuations: Currency values can change between initiation and completion of a transfer, affecting the final received amount.
Regulatory Compliance: International transfers must comply with various national regulations, which may sometimes result in blocked transactions.
The Future of Cross-Border Payments
Emerging financial technologies promise to transform international money transfers. Blockchain solutions and enhanced fraud detection systems may improve both the speed and security of cross-border transactions. These innovations could potentially reduce costs while increasing transparency in global financial flows.
As financial technology continues to evolve, understanding the fundamental mechanisms of international transfers—particularly the proper use of SWIFT/BIC codes—remains essential for both individuals and businesses operating in the global marketplace.