In an era of increasingly globalized financial transactions, the ability to execute international wire transfers with precision has become paramount. SWIFT/BIC codes serve as essential tools in this process, functioning as standardized identifiers that safeguard cross-border payments.
Decoding SWIFT/BIC Identifiers
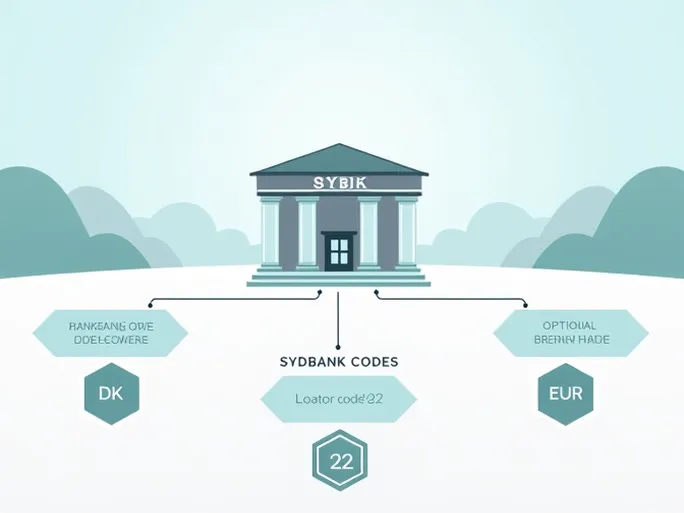
These alphanumeric codes, typically spanning 8 to 11 characters, provide precise identification of financial institutions worldwide. Consider the example of SYDBANK A/S with its SWIFT/BIC code SYBKDK22EUR:
- Institution Code (SYBK) : The first four letters uniquely identify SYDBANK A/S
- Country Code (DK) : The subsequent two letters designate Denmark as the bank's location
- Location Code (22) : These two characters specify the bank's exact geographical position
- Branch Identifier (EUR) : The optional final three characters pinpoint specific branches
Notably, the suffix 'XXX' may denote a bank's headquarters. For instance, SYDBANK A/S's primary code appears as SYBKDK22, while the complete version includes the branch designation (SYBKDK22EUR).
The Imperative of Accuracy
Meticulous verification of SWIFT codes proves critical for international transactions, as errors can result in costly delays or permanent fund loss. Financial experts recommend these essential verification steps:
- Institutional verification : Cross-check the recipient bank's legal name against the SWIFT code registry
- Branch confirmation : When using branch-specific codes, validate the exact branch location
- Geographical validation : Confirm the destination country, as banks with identical names may operate in multiple jurisdictions
These precautions significantly reduce operational risks in international fund transfers. Mastery of SWIFT/BIC protocols not only enhances transactional security but also establishes a foundation for efficient global commerce. Thorough verification of payment details remains the most effective safeguard against financial mishaps.
Conclusion
SWIFT/BIC codes function as both institutional passports and protective mechanisms in international banking. Proper understanding and application of these identifiers enables businesses and individuals to navigate complex cross-border transactions with confidence and precision.