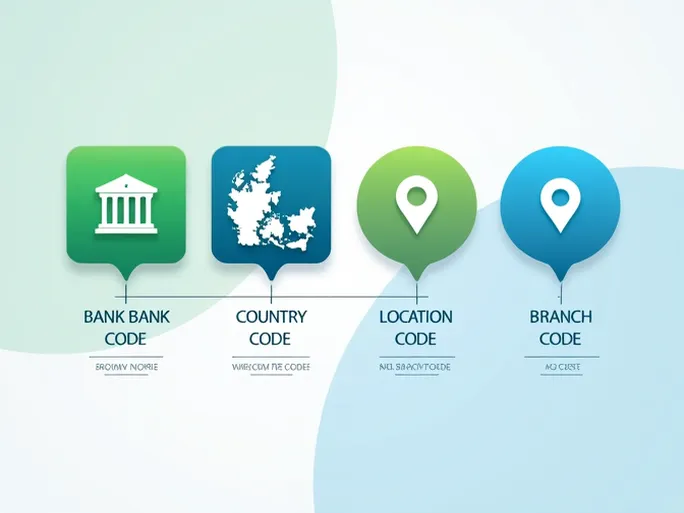
In global financial transactions, the accuracy of SWIFT/BIC codes serves as the backbone of secure cross-border payments. These alphanumeric sequences—often overlooked by casual users—contain meticulously structured information that ensures funds reach their intended destinations efficiently.
Consider the example of SYDBANK A/S, whose SWIFT/BIC code SYBKDK22CPH reveals multiple layers of identification. The initial four letters ( SYBK ) function as the bank code, uniquely identifying SYDBANK A/S. The subsequent two-letter country code ( DK ) confirms the institution's Danish location. Following this, the two-digit location code ( 22 ) pinpoints the bank's headquarters, while the final three letters ( CPH ) specify its Copenhagen branch.
This standardized structure enables financial institutions worldwide to process transactions with precision. A single erroneous character can trigger delays, additional fees, or failed transfers—consequences that underscore the importance of meticulous code verification.
Financial professionals emphasize that validating SWIFT/BIC codes against recipient bank details constitutes a non-negotiable step in international money transfers. The diversity of codes among headquarters and branches necessitates careful cross-checking to confirm alignment with the beneficiary's country, bank name, and specific branch location.
As global payment volumes continue to rise, understanding and verifying these identifiers remains fundamental to maintaining transaction integrity. Institutions and individuals alike must treat code confirmation as an essential safeguard—one that protects against operational disruptions and ensures the smooth movement of capital across borders.