In today's globalized financial landscape, selecting the correct banking codes has become paramount for secure and efficient cross-border transactions. SWIFT/BIC codes serve as more than just alphanumeric sequences—they function as essential bridges between international financial institutions, facilitating rapid and secure fund transfers. As international trade and cross-border financing activities continue to expand, understanding and accurately using these codes has grown increasingly vital.
Understanding SWIFT/BIC Code Structure
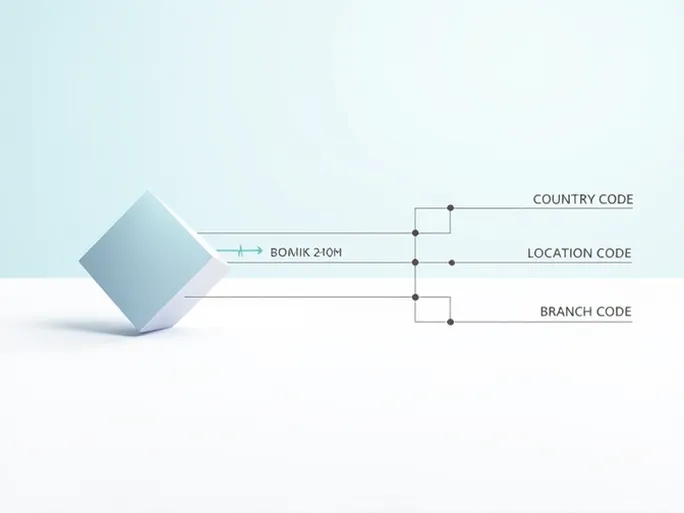
The SWIFT/BIC code (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication/Business Identifier Code) consists of 8 to 11 characters that uniquely identify banks and their branches worldwide. For both consumers and businesses, accurate SWIFT/BIC codes directly impact transaction efficiency and fund security.
Taking ABANCA CORPORACION BANCARIA, S.A. as an example, its SWIFT/BIC code CAGLESMMBOI demonstrates the standard structure:
- First 4 characters (CAGL): Bank code identifying ABANCA CORPORACION BANCARIA, S.A.
- Next 2 characters (ES): Country code (Spain) as defined by ISO standards
- Following 2 characters (MM): Location code indicating the bank's geographical position
- Final 3 characters (BOI): Branch identifier (or XXX for headquarters)
Operational Significance in International Banking
Each component of the SWIFT/BIC code serves critical functions in global financial operations. The bank code prevents confusion among similarly named institutions, while country codes enable quick identification of jurisdictional and regulatory environments. Location codes facilitate efficient routing, and branch identifiers ensure precise fund delivery to specific operational units.
Incorrect usage of these codes can lead to transaction delays, misdirected funds, and potential financial complications. Financial institutions often provide verification tools and comprehensive databases to assist customers in confirming accurate SWIFT/BIC information before initiating transfers.
Impact on Business Transactions
For corporate entities engaged in international commerce, proper SWIFT/BIC code implementation enhances payment processing speed and operational reliability. A single coding error can disrupt cash flows, delay supplier payments, and create unnecessary operational challenges.
Complete banking information—including physical addresses and branch details—further strengthens transaction security and efficiency. For ABANCA CORPORACION BANCARIA, S.A., this includes:
- Primary SWIFT code: CAGLESMM
- Branch code: BOI
- Registered address: PS. RECOLETOS 4, FLOOR 3, MADRID
Understanding these elements enables businesses to navigate international transactions with greater confidence and precision, while also mitigating potential fraud risks.
Strategic Considerations for Global Transactions
Beyond code verification, successful international transfers require awareness of foreign exchange conditions, fee structures, and payment methodologies. These factors collectively influence transaction costs and financial outcomes, making comprehensive preparation essential for optimal financial decision-making.
As global financial integration deepens, mastery of SWIFT/BIC protocols has transitioned from specialized knowledge to fundamental financial literacy. The system's standardized approach continues to streamline international banking communications while reducing operational risks—a critical infrastructure supporting worldwide economic activity.