In today's globalized financial landscape, the demand for international money transfers continues to rise. Whether for business transactions, personal remittances, or investments, ensuring the security and accuracy of fund transfers has become increasingly critical. However, many individuals still face complexities and uncertainties during cross-border transactions, with the use of SWIFT/BIC codes being a common challenge. This is particularly true when sending money to Lebanon in the Middle East, where confusion often arises about correctly applying these codes. Understanding relevant codes, such as the SWIFT code PMAPPS22 ACH for the Palestine Monetary Authority, is essential for anyone engaging in international transfers.
Understanding SWIFT Codes
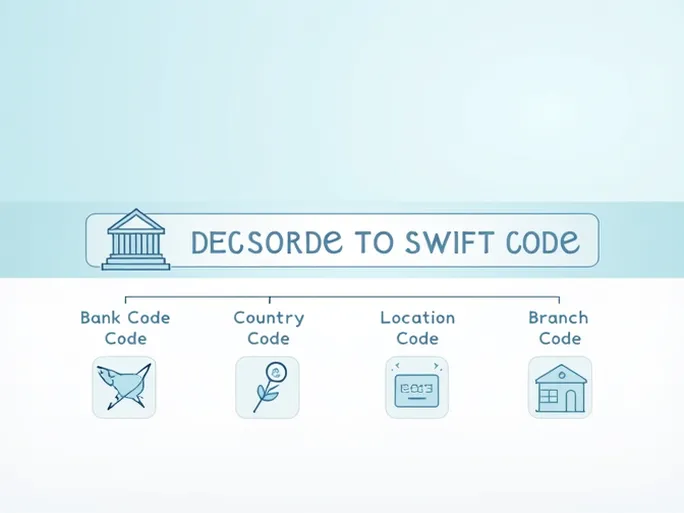
A SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) code, also known as a BIC (Bank Identifier Code), is a unique identifier used to recognize specific financial institutions worldwide. Typically consisting of 8 to 11 characters, the format is structured as AAAA BB CC DDD. The first four letters represent the bank code, followed by a two-letter country code, then a two-digit location code, and finally an optional three-digit branch code. For example, in the code PMAPPS22 ACH:
- PMAP identifies the Palestine Monetary Authority.
- PS denotes the country (Palestine).
- 22 indicates the bank's regional location.
- ACH refers to a specific payment system or branch, such as the Automated Clearing House.
The Role of the Palestine Monetary Authority
The Palestine Monetary Authority serves as the central bank of Palestine, overseeing the nation's monetary system and ensuring financial stability. As the primary regulatory body, it formulates monetary policies and supervises the banking sector. For international transactions, the SWIFT code PMAPPS22 ACH plays a pivotal role in guaranteeing that funds reach their intended destination securely and accurately. Recognizing the functions of this institution helps senders better understand the transaction pathway and mitigate potential risks.
Ensuring Transfer Security
While advancements in digital technology have streamlined international transfers, security concerns persist. The use of SWIFT codes significantly reduces the risk of funds being misdirected. By accurately providing the recipient's SWIFT code, banks can verify the beneficiary's identity, enhancing transaction security.
In practice, banks require customers to input the correct SWIFT code when initiating transfers. Errors in this step may result in funds being sent to the wrong account or, in some cases, becoming irretrievable. Therefore, verifying and correctly entering the code PMAPPS22 ACH is crucial.
The International Transfer Process with SWIFT/BIC Codes
When initiating an international transfer, the SWIFT/BIC code is a fundamental component. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Selecting the Bank and Recipient: Confirm the recipient's bank details, including their account number and SWIFT/BIC code.
- Completing the Transfer Form: Accurately fill out the bank's transfer form with the recipient's name, account number, and SWIFT code (e.g., PMAPPS22 ACH).
- Reviewing Fees: Understand the transaction fees, including any intermediary bank charges, to avoid unexpected deductions.
- Submitting the Request: After verifying all details, submit the transfer request for processing.
Decoding SWIFT Code Details
Beyond facilitating transfers, SWIFT codes convey essential bank information. For PMAPPS22 ACH:
- PMAP: Identifies the Palestine Monetary Authority, emphasizing its regulatory role.
- PS: The country code ensures funds are routed to Palestine.
- 22: The location code helps pinpoint the bank's geographic area.
- ACH: Specifies the payment system, streamlining electronic transfers.
Choosing the Correct SWIFT Code
Accuracy is paramount when selecting a SWIFT code. For transactions involving Palestine, PMAPPS22 ACH is indispensable. Always verify that the code is up-to-date and validated before proceeding. Note that codes ending with "XXX" typically represent a bank's headquarters rather than a specific branch, which may cause delays if used incorrectly.
Challenges in Cross-Border Transactions
International transfers can present hurdles such as delays, misrouted funds, or compliance with sanctions. Familiarity with codes like PMAPPS22 ACH helps users navigate these complexities. Some countries impose restrictions on transactions from specific regions, necessitating prior research or consultation with financial experts to ensure smooth processing.
Legal Compliance in International Transfers
Adhering to international and local regulations is critical. For instance, certain jurisdictions may require declarations for transfers exceeding specific amounts. Staying informed about SWIFT code updates and compliance requirements is a shared responsibility between banks and customers.
Best Practices for Successful Transfers
To optimize international transfers:
- Double-check recipient details, including the SWIFT code.
- Clarify fee structures, especially for intermediary banks.
- Request a transaction receipt for tracking purposes.
- Maintain communication with the recipient to confirm fund arrival.
- Monitor the transfer status through your bank's platform.
Conclusion
Whether for personal or business purposes, correctly using SWIFT/BIC codes like PMAPPS22 ACH is vital for secure and efficient cross-border transactions. As global financial interactions grow, mastering these details empowers individuals and businesses to navigate international banking with confidence, minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.