In today’s increasingly globalized financial landscape, international wire transfers have become a vital component of daily economic activities for individuals and businesses alike. At the heart of this process lies the SWIFT/BIC code—a seemingly simple combination of letters and numbers that serves as a cornerstone for secure and accurate transactions.
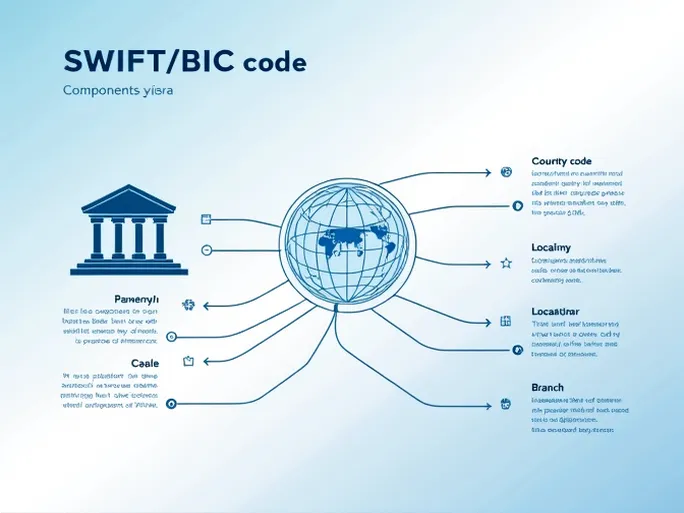
A SWIFT/BIC code typically consists of 8 to 11 characters, each segment carrying specific identifying information. For example, consider the code for Taiwan Cooperative Bank Ltd (TACBTWTP011):
- Bank code (TACB) : These four letters uniquely identify the financial institution within Taiwan.
- Country code (TW) : The two-letter designation ensures transactions are routed to the correct nation—in this case, Taiwan.
- Location code (TP) : This segment pinpoints the bank’s headquarters, guiding funds to their proper destination.
- Branch code (011) : The three-digit suffix specifies a particular branch, with "XXX" typically representing the head office.
Accuracy in using SWIFT codes cannot be overstated. To prevent costly errors or processing delays, financial institutions recommend these verification steps:
- Confirm bank name : Cross-check that the entered financial institution name matches exactly with the recipient’s bank records.
- Verify branch details : When using a branch-specific code, ensure alignment with the recipient’s actual banking location.
- Validate country information : With many banks operating internationally, confirming the SWIFT code’s country alignment prevents misdirected transfers.
Proper utilization of SWIFT/BIC codes provides a reliable safeguard for international money transfers. For both individual and corporate users, understanding this system represents a fundamental step toward ensuring financial transaction security in global commerce.