In today's globalized economy, international financial transactions have become increasingly frequent, with cross-border fund transfers forming an essential part of daily operations for both businesses and individuals. As globalization advances, more people need to conduct international wire transfers through banks, where the accuracy of SWIFT/BIC codes plays a pivotal role. This article examines the structure and importance of SWIFT/BIC codes, along with best practices for ensuring their correct usage to minimize potential delays and errors.
Understanding SWIFT/BIC Code Structure
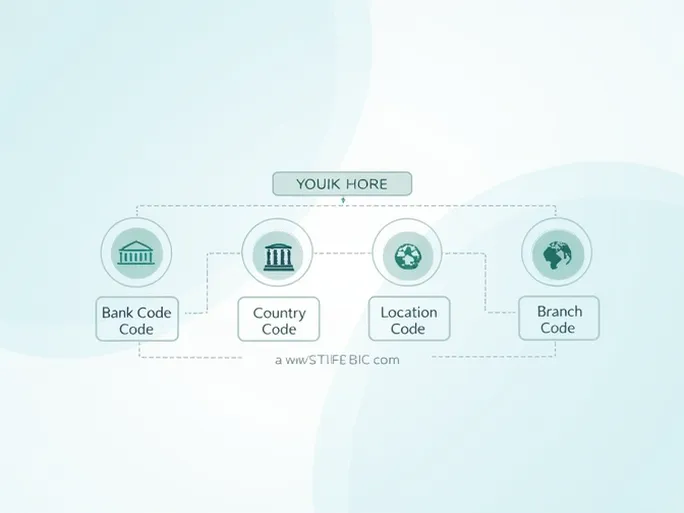
The SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) code, also known as BIC (Business Identifier Code), serves as a unique identifier for communication and fund transfers between banks. Each SWIFT code consists of 8 to 11 characters.
For example, Taiwan Cooperative Bank Ltd's SWIFT/BIC code is TACBTWTP015. This code can be broken down into distinct components:
- Bank Code (TACB): The first four letters represent the specific bank. In this case, "TACB" stands for Taiwan Cooperative Bank.
- Country Code (TW): The next two letters indicate the bank's country. "TW" represents Taiwan, helping senders verify the recipient bank's location.
- Location Code (TP): These two characters specify the bank's headquarters or primary operational center.
- Branch Code (015): The final three digits identify specific branches. A code ending with "XXX" typically refers to a bank's head office.
The Importance of Accurate SWIFT Codes
In international transfers, SWIFT/BIC codes serve not just as bank identifiers but as critical safeguards for secure and efficient fund movement. Incorrect codes may cause failed transactions or misdirected funds, potentially creating serious complications for both senders and recipients. A single character error could divert funds to unintended accounts, possibly triggering legal complications. Transactors must therefore treat this detail with utmost care.
Verifying SWIFT Code Accuracy
Before initiating international transfers, verifying SWIFT code correctness is essential. Consider these practical measures:
- Confirm bank names: Ensure the recipient bank's official name matches exactly, as similar names may belong to different institutions with distinct codes.
- Check branch specifics: When transferring to particular branches, verify their unique SWIFT codes, as these differ from head office identifiers.
- Validate country codes: Cross-check the two-letter country designation to prevent accidental transfers to foreign banks with similar names.
- Consult official sources: Bank websites and customer service departments typically provide authoritative SWIFT code information.
- Review community insights: Online forums and social media platforms may offer user experiences that help validate code accuracy.
Code Updates and Modifications
SWIFT/BIC codes aren't permanent; banks may modify them during reorganizations or other operational changes. Regularly confirming code validity through official channels helps prevent transaction issues stemming from outdated information.
Evolution of SWIFT Systems
Technological advancements continue transforming international banking infrastructure. Initiatives like SWIFT gpi (Global Payments Innovation) enhance transfer speed and transparency through improved tracking capabilities. These developments are gradually reducing errors associated with code inaccuracies while optimizing cross-border payment efficiency.
In international finance, precise SWIFT/BIC codes form the foundation for seamless transactions. By methodically verifying bank details, branch specifics, and country codes through reliable sources, transactors can significantly mitigate risks. As financial systems evolve, maintaining awareness of SWIFT code updates ensures transactions proceed smoothly, safeguarding funds until they reach intended destinations.