In an increasingly globalized world, international money transfers have become commonplace, whether for personal remittances or business transactions. However, what might appear as a straightforward process often encounters delays or failures due to overlooked details. Among these, the SWIFT/BIC code stands out as a critical element ensuring secure and efficient cross-border fund transfers.
Understanding SWIFT/BIC Codes
The SWIFT/BIC code—an acronym for Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication and Bank Identifier Code —serves as a unique identifier for financial institutions worldwide. This alphanumeric code enables banks to exchange information accurately, facilitating timely and secure transactions. For individuals and businesses conducting international transfers, the accuracy of this code directly impacts the efficiency of fund transfers.
Structure of SWIFT/BIC Codes
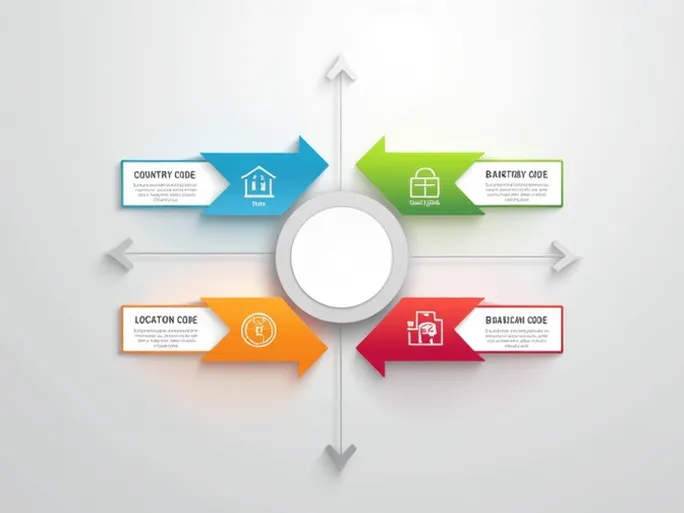
Comprising 8 to 11 characters, each segment of a SWIFT/BIC code conveys specific information:
- Bank Code (4 characters): A unique identifier for the financial institution (e.g., "TACB" for Taiwan Cooperative Bank).
- Country Code (2 characters): An ISO 3166-1 standard code indicating the bank's country (e.g., "TW" for Taiwan).
- Location Code (2 characters): Specifies the bank's headquarters location (e.g., "TP" for Taipei).
- Branch Code (3 characters, optional): Identifies specific branches (e.g., "017" for a particular branch).
Case Study: Taiwan Cooperative Bank's SWIFT/BIC Code
As one of Taiwan's largest financial institutions, Taiwan Cooperative Bank plays a significant role in international transactions. Its SWIFT/BIC code, TACBTWTP017 , exemplifies how these codes ensure precise fund routing:
- TACB: Identifies Taiwan Cooperative Bank.
- TW: Denotes Taiwan as the country.
- TP: Specifies Taipei as the location.
- 017: Indicates a specific branch, reducing transfer errors.
Best Practices for Using SWIFT/BIC Codes
To ensure seamless international transfers, consider these steps:
- Verify the recipient's SWIFT/BIC code: Confirm the code directly with the recipient or their bank to avoid errors.
- Gather comprehensive details: Collect the recipient's bank name, branch address, and account number.
- Select the appropriate transfer method: Choose between standard or expedited services based on urgency and amount.
- Understand fees: Be aware of potential charges that may affect the final amount received.
- Maintain communication: Notify the recipient once the transfer is initiated.
- Keep records: Save transaction receipts for future reference or dispute resolution.
Security Considerations
SWIFT/BIC codes are not just about accuracy—they are integral to financial security. The SWIFT network employs robust encryption to protect transaction data, ensuring confidentiality and reducing fraud risks. This system is widely adopted by global financial institutions to maintain secure and anonymous transactions.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite precautions, issues may arise:
- Delayed transfers: Contact your bank for updates if the transaction exceeds expected processing times.
- Failed transfers: Verify the recipient's account details and SWIFT/BIC code if funds don't arrive.
- Incorrect codes: Immediate bank intervention is required if funds are sent to the wrong institution.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of SWIFT/BIC codes is essential for anyone engaged in international banking. Taiwan Cooperative Bank's code, TACBTWTP017, demonstrates how these identifiers safeguard transactions. By meticulously verifying codes and understanding their structure, individuals and businesses can minimize errors and enhance the efficiency of cross-border payments. This knowledge empowers users to navigate global finance with confidence, ensuring timely and secure fund transfers.