In global financial transactions, SWIFT/BIC codes play an indispensable role. These alphanumeric sequences serve not just as bank identifiers but as crucial elements ensuring the smooth processing of international money transfers.
The Anatomy of SWIFT/BIC Codes
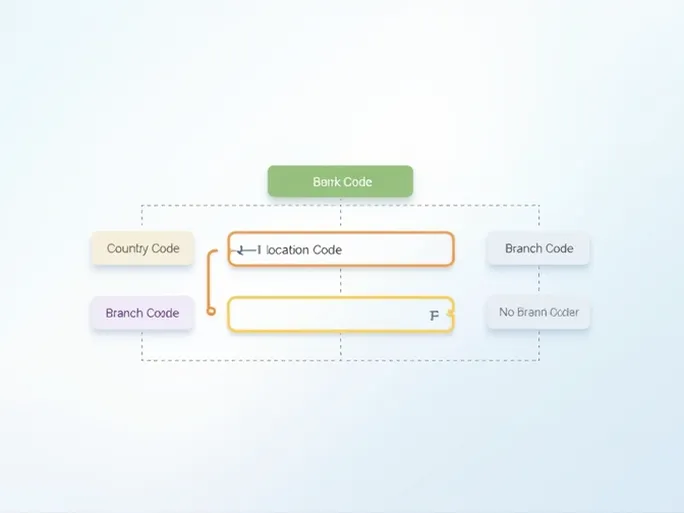
The structure of SWIFT/BIC codes appears simple yet contains significant information within its 8 to 11 characters. The first four letters typically represent the bank code, identifying the financial institution. For instance, the code "TACB" would indicate Taiwan Cooperative Bank.
Following the bank identifier comes the two-letter country code (such as "TW" for Taiwan), precisely locating the bank's jurisdiction. The next two characters (letters or digits) specify the bank's headquarters location, while the optional final three digits identify specific branches.
Why Accuracy Matters in International Transfers
During international wire transfers, the precision of SWIFT codes becomes paramount. Any discrepancy can lead to processing delays or failed transactions. Financial experts emphasize several verification steps:
- Bank Verification: Cross-check the bank name with the recipient's provided information.
- Branch Confirmation: When using a branch-specific SWIFT code, verify the recipient's actual branch affiliation.
- Country Validation: Ensure the SWIFT code corresponds to the destination country, as multinational banks operate across borders.
Financial institutions worldwide process millions of transactions daily using this standardized system. The SWIFT network's reliability and security have made it the backbone of international banking since its establishment in 1973.

