In today's increasingly interconnected financial world, international wire transfers have become a routine part of global commerce and personal finance. Ensuring your funds reach their intended destination safely and efficiently requires understanding one critical element: the SWIFT/BIC code.
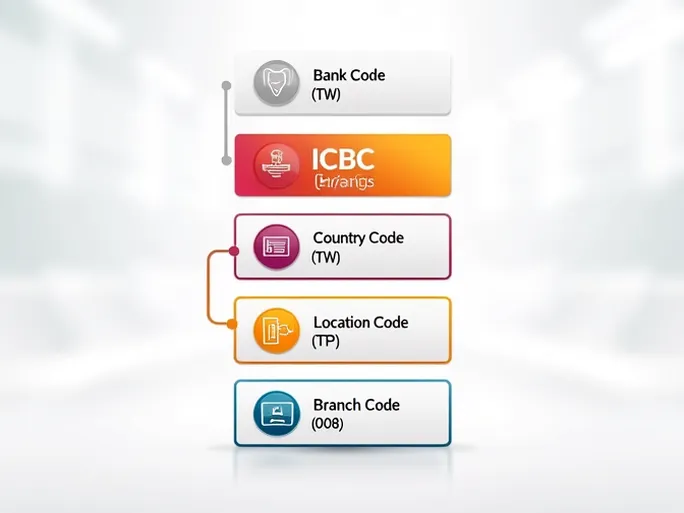
These unique identifiers, composed of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters, serve as precise addresses for financial institutions worldwide. Examining the structure of MEGA International Commercial Bank's code (ICBCTWTP008) reveals how these codes function:
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
- Bank Code (ICBC): The first four letters identify the specific financial institution.
- Country Code (TW): The subsequent two letters indicate the bank's registered country (Taiwan in this example).
- Location Code (TP): These characters pinpoint the bank's headquarters or primary office location.
- Branch Code (008): The final three digits specify a particular branch, with "XXX" typically denoting the institution's headquarters.
Best Practices for Secure Transfers
To minimize errors and ensure successful transactions, financial experts recommend these verification steps:
- Bank Name Verification: Confirm the recipient bank's exact legal name matches your records.
- Branch-Specific Codes: When using a branch-specific identifier, double-check that it corresponds to the recipient's account location.
- Geographical Accuracy: Verify that the country code aligns with the destination bank's registered jurisdiction.
Whether conducting personal remittances or corporate financial operations, proper use of SWIFT/BIC codes remains fundamental to navigating the complexities of international banking. This standardized system provides the reliability and precision required for cross-border transactions in our globalized economy.