Have you ever experienced delays in international money transfers due to incorrect or missing bank identification codes? This common challenge in global finance highlights the critical importance of understanding and properly using SWIFT/BIC codes, especially for cross-border transactions. This article examines the structure of BANQUE MISR's SWIFT/BIC code to help navigate this essential financial tool.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC System
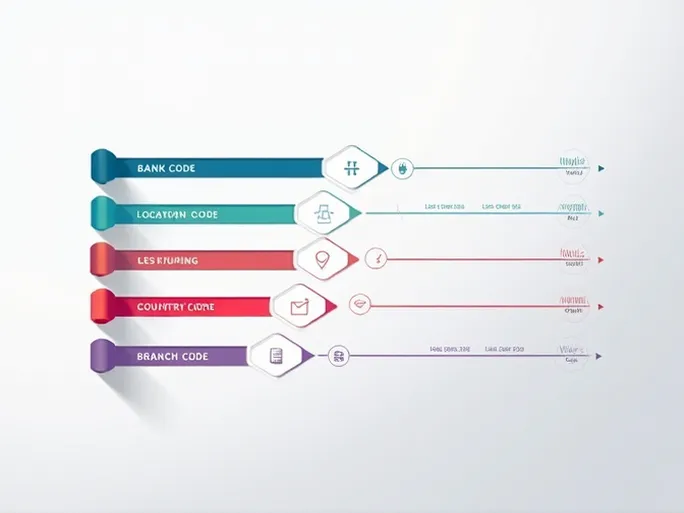
The SWIFT/BIC code, also known as the international bank identifier code, consists of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters that uniquely identify financial institutions worldwide. The code structure contains several key components:
- Bank Code (4 letters): For BANQUE MISR, this appears as "BMIS"
- Country Code (2 letters): "EG" identifies Egypt as the bank's home country
- Location Code (2 characters): "CX" indicates the bank's headquarters location
- Branch Code (3 characters, optional): Specific branch identifiers like "TRF"
Essential Verification Steps
When processing international transfers, the terminal "XXX" in a BIC code typically refers to a bank's head office. To ensure seamless transactions, financial experts recommend these verification measures:
- Bank Name Confirmation: Verify the institution name matches the recipient's bank exactly
- Branch Accuracy: When using branch-specific codes, confirm alignment with the recipient's branch
- Country Verification: Ensure the SWIFT code corresponds to the correct destination country
Proper understanding of SWIFT/BIC codes enhances transaction efficiency and contributes to smoother international financial operations. As global commerce continues to expand, mastery of these banking identifiers provides a fundamental advantage in cross-border financial management.