International wire transfers are a cornerstone of global commerce, but delays or errors can disrupt transactions. These issues often stem from incorrect or incomplete SWIFT/BIC codes, the standardized identifiers for banks and their branches worldwide.
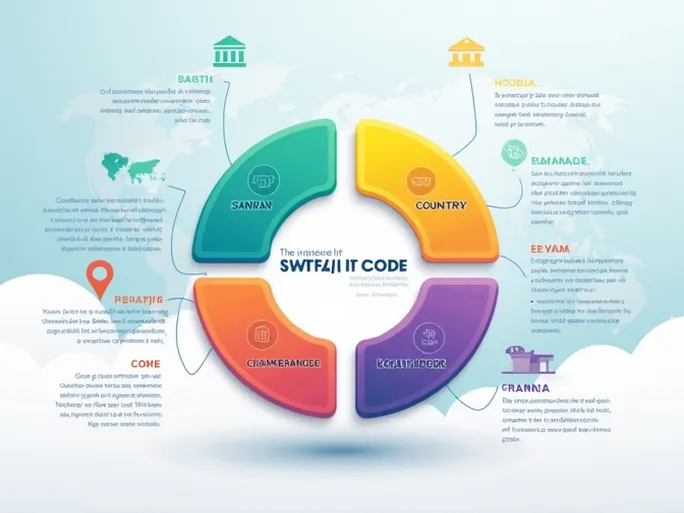
SWIFT/BIC codes consist of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters. For example, the code ROYCCAT2HIC breaks down as follows:
- ROYC identifies the Royal Bank of Canada
- CA denotes the country (Canada)
- T2 is the location code for the bank’s headquarters
- HIC specifies a particular branch
Codes ending with XXX typically indicate a bank’s primary office, which may be preferable for certain transactions.
Key Verification Steps
To minimize transfer issues, recipients and senders should confirm the following details:
- Bank Name: Ensure the recipient’s bank matches the SWIFT code’s institution.
- Branch Specificity: If using a branch-specific code, verify it aligns with the recipient’s account location.
- Country Accuracy: Cross-check that the code corresponds to the correct country, as multinational banks operate across borders.
Precise code usage reduces processing errors and accelerates fund delivery. Financial institutions recommend double-checking these identifiers before initiating transfers.