In global financial transactions, SWIFT/BIC codes serve as critical tools for ensuring the accurate and swift transfer of funds. When conducting international wire transfers, selecting the correct bank and its corresponding code is essential. For the Royal Bank of Canada (RBC), the SWIFT/BIC code ROYCCAT2CLS precisely identifies the institution and its position within the international financial system. This report examines the structure and practical applications of this code to help users navigate cross-border transactions with confidence.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
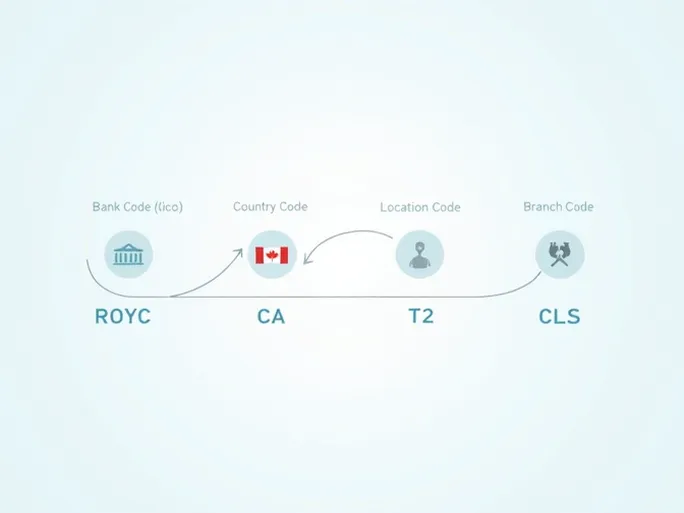
A SWIFT/BIC code consists of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters, systematically divided into four components:
- Bank Code (ROYC): The first four letters uniquely identify the Royal Bank of Canada.
- Country Code (CA): The subsequent two letters denote Canada as the bank’s home country.
- Location Code (T2): This segment specifies the bank’s headquarters or primary operational base.
- Branch Code (CLS): The final three characters pinpoint a specific branch. An "XXX" suffix indicates the bank’s head office.
Thus, RBC’s complete SWIFT/BIC code, ROYCCAT2CLS , reflects its institutional identity, national jurisdiction, and operational footprint. Mastery of this code helps clients avoid transfer delays while enhancing the security and efficiency of cross-border payments.
Practical Implications for Users
In multinational transactions, the correct application of SWIFT codes is nonnegotiable. Errors in code entry may result in misdirected funds or processing bottlenecks, potentially incurring financial losses. Additionally, understanding the code’s composition enables users to recognize analogous formats when interacting with other financial institutions.
As international banking grows increasingly interconnected, fluency in SWIFT/BIC protocols becomes indispensable. Users are advised to verify these identifiers before initiating transfers, ensuring seamless and secure movement of capital across borders.