In today’s globalized financial landscape, cross-border money transfers have become a routine part of life for individuals and businesses alike. Yet, when sending funds internationally, ensuring the secure and timely arrival of money in the recipient’s account hinges on one often-overlooked detail: the SWIFT/BIC code.
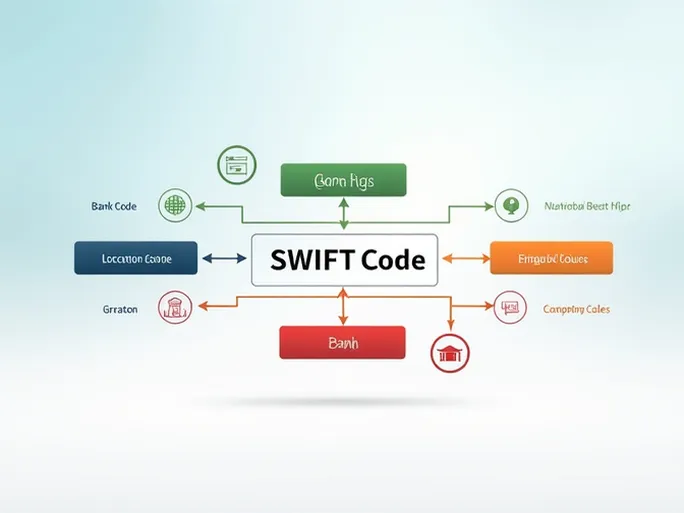
A SWIFT/BIC code is a standardized combination of 8 to 11 alphanumeric characters used to identify financial institutions worldwide. Take the code ITAUCLRMXXX as an example. Its structure breaks down as follows:
- Bank code (ITAU) : The first four letters represent the receiving bank’s name—in this case, Banco Itaú Chile.
- Country code (CL) : The next two letters indicate the bank’s home country (CL for Chile).
- Location code (RM) : These two characters specify the bank’s headquarters region.
- Branch code (XXX) : The final three digits identify a specific branch. If the code ends with "XXX," the funds are routed to the bank’s head office rather than a particular branch.
Using the correct SWIFT/BIC code is essential for international transfers. Accuracy not only expedites processing but also minimizes errors and delays.
Before initiating a transfer, verify the following:
- Bank details : Confirm that the recipient bank’s name matches the information provided.
- Branch information : If using a branch-specific SWIFT code, ensure it corresponds to the recipient’s account branch.
- Country consistency : The SWIFT code’s country designation must align with the recipient bank’s location to avoid transfer failures.
While cross-border payments offer convenience, the importance of accurate SWIFT/BIC codes cannot be overstated. A clear understanding of these details ensures funds reach their destination securely and without unnecessary delays.