In an increasingly globalized world, international money transfers have become more frequent than ever. This trend not only facilitates financial flows between individuals and businesses but also significantly enhances global economic connectivity. However, this growth has also brought heightened demands for secure and efficient fund transfers, particularly in cross-border transactions.
Have you ever wondered how to ensure your money reaches the intended bank account safely and accurately? This article explores CRDB Bank's SWIFT code and its crucial role in international money transfers, empowering you to navigate every transaction with confidence.
Decoding the SWIFT System
SWIFT codes (officially known as Bank Identifier Codes or BIC) serve as standardized identifiers for financial institutions worldwide. These codes enable efficient and accurate transactions between banks across different countries and regions. With the correct SWIFT code, you can transfer funds to any bank globally.
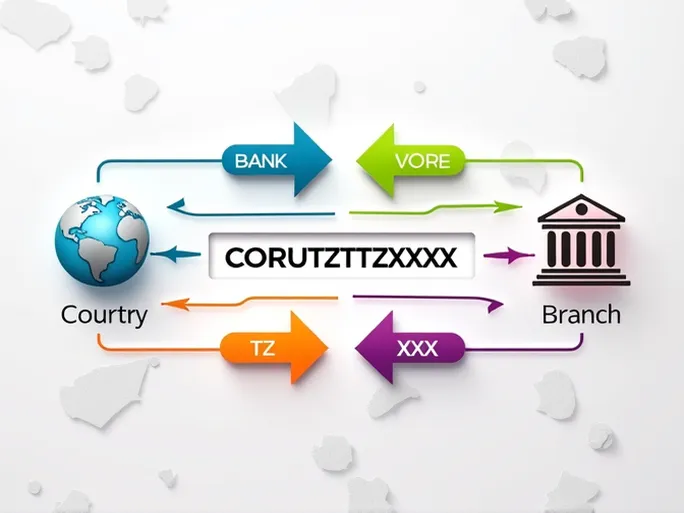
CRDB Bank, one of Tanzania's leading commercial banks serving both individual and corporate clients, uses the SWIFT code CORUTZTZXXX . This alphanumeric combination contains precise information about the bank and its location, simplifying what could otherwise be a complex transfer process.
Anatomy of a SWIFT Code
The structure of SWIFT codes follows strict standardization, consisting of 8 to 11 characters with specific meanings:
- Bank Code (4 letters - CORU): The first four letters uniquely identify the financial institution. For CRDB Bank, 'CORU' ensures all transaction messages are accurately directed.
- Country Code (2 letters - TZ): These letters represent the bank's home country using ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 standards. 'TZ' denotes Tanzania.
- Location Code (2 letters - TZ): This indicates the bank's geographic location within the country. While 'TZ' in this case doesn't specify a particular city, it confirms the bank's Tanzanian presence.
- Branch Code (3 characters - XXX): The final component identifies specific branches. 'XXX' typically represents a bank's headquarters, while other codes would indicate particular branches.
Essential Considerations for International Transfers
Beyond SWIFT codes, several critical factors influence international money transfers:
Transaction Fees: Banks and transfer services have varying fee structures. Comparing costs across providers can lead to significant savings, especially for frequent transfers.
Exchange Rates: Currency fluctuations between transfer initiation and completion can affect the final received amount. Some institutions offer rate-locking services to mitigate this risk.
Processing Times: Transfers typically require 1-5 business days. Avoiding holidays and weekends can prevent unnecessary delays. Maintaining communication with recipients helps confirm successful transfers.
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying financial regulations. Some jurisdictions impose additional verification requirements for large transactions, potentially extending processing times.
The Digital Transformation of Cross-Border Payments
Modern financial technology has simplified international transfers through user-friendly digital platforms. While these innovations have made the process more accessible, the fundamental importance of accurate SWIFT codes remains unchanged. This underscores the continued need for attention to detail in every transaction.
For both personal and commercial transactions, whether sending money to family abroad or conducting international business, correct SWIFT codes serve as essential safeguards for secure fund transfers.