In the complex landscape of cross-border payments, ensuring funds arrive safely and promptly remains every user's primary concern. As global economic integration continues, international trade has become increasingly frequent, making the selection of appropriate financial instruments crucial for both individuals and businesses engaged in transnational transactions. Among these tools, proper use of SWIFT codes serves not only as a critical guarantee for successful fund transfers but also represents an indispensable instrument in international financial operations.
Decoding the Structure of SWIFT/BIC Codes
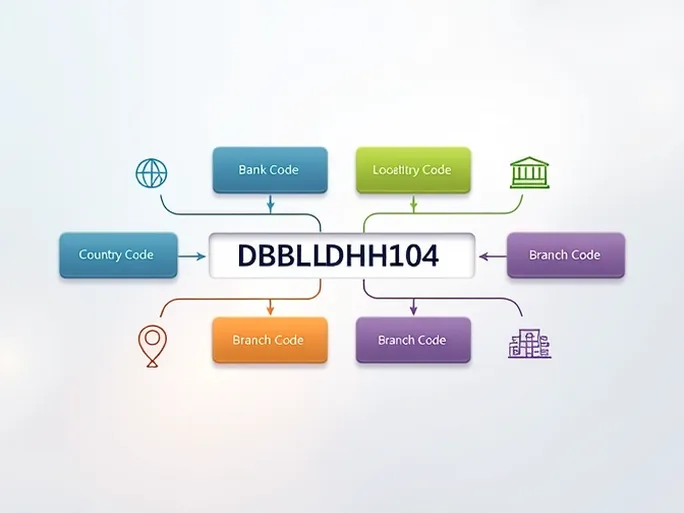
The SWIFT/BIC (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) code serves as a standardized format for identifying banks and financial institutions globally. Typically comprising 8 to 11 characters, each segment carries distinct significance and performs vital functions.
Taking DBBLBDDH104 as an example - the code for DUTCH-BANGLA BANK PLC. - we can analyze its four structural components:
- Bank Code (DBBL): The initial four letters represent the specific banking institution. In this case, DBBL identifies DUTCH-BANGLA BANK PLC., a major Bangladeshi commercial bank established in 1996 that provides comprehensive banking services.
- Country Code (BD): The subsequent two letters denote the bank's home country using ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 standards. BD signifies Bangladesh, ensuring funds route to the correct nation.
- Location Code (DH): These two characters pinpoint the bank's headquarters location within Bangladesh, enabling geographical identification of the account's origin.
- Branch Code (104): The final three digits specify a particular branch. When ending with XXX, the code typically refers to the bank's headquarters rather than a specific branch.
This systematic design ensures each SWIFT/BIC code uniquely identifies financial institutions worldwide. Despite emerging financial technologies and transfer methods, SWIFT codes maintain their position as fundamental instruments for cross-border payments due to their standardized nature and universal adoption.
Optimal Use Cases for DBBLBDDH104
When initiating international transfers to DUTCH-BANGLA BANK PLC., users must employ the correct SWIFT code (DBBLBDDH104). This identifier not only confirms the bank's identity but also safeguards transaction security and timeliness. Whether for personal remittances or corporate transactions, accurate SWIFT code usage significantly reduces operational risks and prevents delays or misdirected funds.
Common application scenarios include:
- Personal Transfers: Supporting family members abroad or paying international tuition fees requires precise SWIFT codes to ensure prompt delivery.
- Business Payments: International procurement processes benefit from correct SWIFT codes, accelerating supplier payments and enhancing cash flow management.
- Property Investments: Individuals and corporations engaging in overseas real estate transactions minimize processing time through proper SWIFT code implementation.
Users should note that international transfers are subject to varying national regulations. Understanding relevant legal frameworks before initiating transactions ensures smooth operations.
The Critical Importance of SWIFT Code Verification
Confirming SWIFT code accuracy before any international transfer remains paramount. Incorrect codes may result in undelivered funds or require extensive recovery procedures. Always verify codes through official banking channels or direct institution consultation.
Additional considerations include:
- Understanding bank policies: Fee structures, exchange rates, and service terms vary significantly between institutions. Selecting appropriate banks optimizes transfer costs.
- Maintaining transaction records: Preserve all transfer documentation including confirmation emails and receipts to protect financial interests if issues arise.
- Monitoring processing times: Bank-specific processing durations affect fund availability. Awareness facilitates better financial planning.
Enhancing Financial Management Capabilities
Beyond SWIFT code comprehension, users can improve international money management through several practical approaches:
- Selecting appropriate transfer tools: Financial technology advancements offer diverse options beyond traditional bank transfers. Evaluating emerging platforms provides additional solutions.
- Tracking market conditions: Fluctuating exchange rates and fees impact transfer costs. Strategic timing based on market analysis generates savings.
- Conducting risk assessments: Evaluating potential challenges like policy changes or economic instability enables informed decision-making and improves capital efficiency.
Comprehending SWIFT codes represents a fundamental aspect of international payments, but users must complement this knowledge with financial acumen and market awareness. This comprehensive approach ensures secure, efficient cross-border transactions in our increasingly interconnected global economy.