In today's rapidly evolving global financial system, the security and efficient flow of funds have become paramount. Whether for corporate trade transactions or personal international transfers, streamlining financial processes while ensuring security remains central to banking operations. As international remittance demands continue to grow, the SWIFT network has emerged as an essential banking communications tool to facilitate these transactions.
Understanding SWIFT Codes
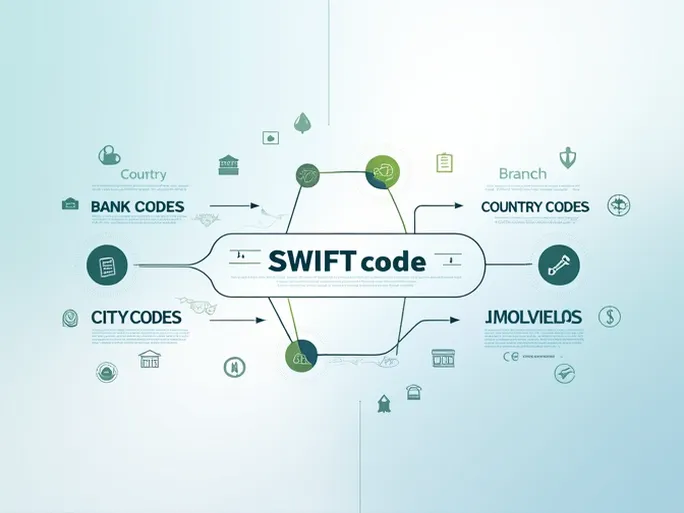
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) provides a standardized messaging network for financial institutions worldwide. A SWIFT code, also known as a Bank Identifier Code (BIC), follows this structure:
- First 4 characters: Bank code (identifies the financial institution)
- Next 2 characters: Country code (ISO country designation)
- Following 2 characters: Location code (city designation)
- Optional final 3 characters: Branch code (specific office designation)
For First Abu Dhabi Bank PJSC (FAB), the SWIFT code NBADAEAAADV breaks down as:
- NBAD : Bank identifier for First Abu Dhabi Bank
- AE : Country code for United Arab Emirates
- AA : Location code for Abu Dhabi
- ADV : Specific branch identifier
The Critical Role of SWIFT Codes in International Transfers
Precise SWIFT code usage proves essential for successful international transactions. Even minor errors can divert funds to incorrect recipients or cause payment delays. The system offers several key advantages:
Transaction Tracking: SWIFT's network enables real-time payment status monitoring, particularly valuable for large commercial transactions where confirmation of receipt triggers subsequent business actions.
Cost Efficiency: Accurate SWIFT codes reduce processing fees by eliminating the need for additional verification procedures that banks apply to unclear transactions. Proper coding streamlines processing and minimizes intermediary charges.
Locating and Verifying SWIFT Codes
For individuals unfamiliar with international banking protocols, SWIFT code verification requires careful attention. Recommended verification methods include:
- Consulting the bank's official website (typically under "Contact" or "Services" sections)
- Using reputable third-party financial information platforms
- Contacting bank customer service for official confirmation
Enhancing Transfer Security
When initiating international transfers, consider these security measures:
- Select established financial institutions with proven transaction security protocols
- Double-check all recipient details including account numbers and SWIFT codes
- Avoid conducting financial transactions over public Wi-Fi networks
- Maintain awareness of evolving financial fraud techniques
- Retain complete transaction records for future reference
Conclusion
SWIFT codes serve as fundamental components of secure international banking, with First Abu Dhabi Bank's NBADAEAAADV code exemplifying this critical infrastructure. Whether for commercial transactions or personal remittances, proper SWIFT code usage combined with verified banking channels ensures efficient, secure fund transfers. Understanding these protocols allows individuals and businesses to navigate global financial systems with confidence, safeguarding their transactions in an increasingly interconnected economic landscape.