In today’s highly globalized economy, cross-border fund transfers have become indispensable for both personal and commercial activities. Whether for individual remittances, international investments, or corporate trade settlements, the rapid movement of money relies heavily on the efficient operation of banking systems. The SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) network was established to address communication challenges between banks in international transactions. Each financial institution has a unique SWIFT/BIC code, which serves not only as its identifier but also as a critical safeguard for accurate and secure cross-border transfers.
Among global financial institutions, First Abu Dhabi Bank PJSC (FAB) stands out for its robust financial strength and international reputation, making it a preferred choice for many clients. Understanding FAB’s SWIFT code— NBADAEAAAAM —is essential for seamless international fund transfers. This code is meticulously structured, with each segment carrying specific information to ensure precision in transactions.
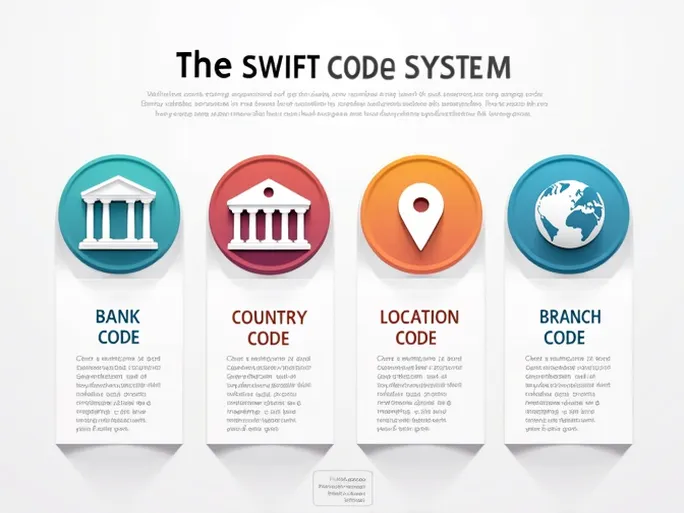
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
1. Bank Code (NBAD): The first four letters, "NBAD," uniquely identify First Abu Dhabi Bank within the SWIFT network. This segment ensures funds are routed to the correct institution. Errors here may result in misdirected transfers, underscoring the need for careful verification.
2. Country Code (AE): The subsequent two letters, "AE," denote the United Arab Emirates, the bank’s home country. Accurate country codes are vital for directing transfers to the right jurisdiction, particularly in a financial hub like the UAE.
3. Location Code (AA): The next two letters, "AA," specify the bank’s operational base, often corresponding to a city or primary office. This detail is crucial for transactions requiring branch-level precision.
4. Branch Code (AAM): The final three letters, "AAM," identify a specific branch or department. While optional for some transfers, this segment can influence processing times and delivery accuracy.
Why SWIFT Codes Matter
Globalization has simplified financial connectivity but introduced complexities like transfer delays, lost funds, or fraud. SWIFT codes mitigate these risks by standardizing cross-border transactions. For example, using FAB’s SWIFT code ( NBADAEAAAAM ) ensures payments to Abu Dhabi-based vendors reach the intended account without intermediaries or errors.
However, successful transfers also require accurate beneficiary details—account numbers, addresses, and transaction references. Omissions or inaccuracies may trigger delays or rejections, even with a correct SWIFT code.
Evolving Technologies and Enduring Standards
While digital banking and blockchain innovations offer alternative remittance channels, SWIFT remains foundational for international transfers. FAB’s integration of traditional codes with modern platforms exemplifies how legacy systems coexist with technological advancements.
Clients should also consider exchange rates, fees, and processing times—especially for large sums—to optimize transfer outcomes. Consulting bank representatives can clarify these variables and minimize risks.
Abu Dhabi’s Financial Ecosystem
As the UAE’s capital, Abu Dhabi boasts a stable economy and sophisticated financial infrastructure. FAB’s global reach and localized services make it a conduit for international capital flows, whether for personal or commercial purposes.
Mastering SWIFT codes like NBADAEAAAAM is more than procedural—it’s a strategic advantage in navigating global finance. For individuals and corporations alike, this knowledge ensures efficient, secure cross-border transactions in an interconnected world.