In today's globalized economy, cross-border transactions have become increasingly common. For businesses and individuals engaging in international commerce or personal fund transfers, understanding the fundamentals of international banking is essential. Among these, the SWIFT/BIC code plays a pivotal role. More than just a unique identifier for banks in international transactions, the SWIFT code ensures secure and efficient fund transfers. This article explores Banque du Caire, one of Egypt's leading financial institutions, and its SWIFT code BCAIEGCX011 , to facilitate seamless cross-border transactions.
Introducing Banque du Caire
Established in 1952, Banque du Caire stands as one of Egypt's oldest and most comprehensive banks. With a broad customer base and a diverse range of financial products, it caters to both individual and corporate clients. The bank offers services including savings accounts, loans, remittances, and investment solutions, addressing the varied needs of its customers. Its extensive domestic and international network makes it a key player in regional and global fund transfers.
The Significance of SWIFT Codes
SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) is the organization responsible for facilitating communication between financial institutions worldwide. The SWIFT code, also known as the BIC (Bank Identifier Code), is an international standard used to identify banks and ensure accurate processing of cross-border transactions. This system enables secure and swift transfers, minimizing errors and delays.
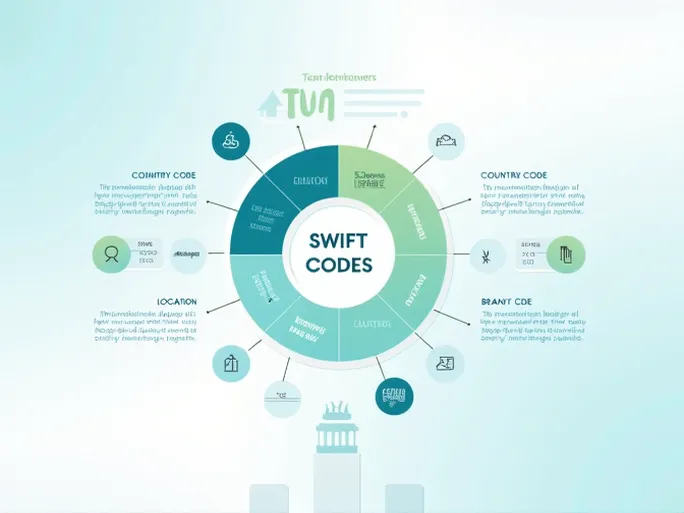
Decoding the SWIFT Code Structure
Understanding the structure of a SWIFT code is crucial for its effective use. Take Banque du Caire's SWIFT code BCAIEGCX011 as an example:
- First four characters (BCAI) : Represent the bank's abbreviated name, uniquely identifying Banque du Caire globally.
- Next two characters (EG) : Denote the country where the bank is located—in this case, Egypt.
- Following two characters (CX) : Indicate the bank's location, typically the city. Here, CX refers to Cairo.
- Last three characters (011) : An optional extension identifying a specific branch. For Banque du Caire, this points to a particular branch in Cairo.
This structured format ensures efficient processing of transactions, reducing the risk of errors and guaranteeing that funds reach their intended destination.
Why SWIFT Codes Matter in International Transfers
When transferring funds to Banque du Caire, providing the correct SWIFT code ( BCAIEGCX011 ) is critical. An incorrect code may result in failed transactions, delayed transfers, or even lost funds, leading to financial complications. Accurate SWIFT codes also expedite processing times, ensuring timely delivery of funds. Conversely, errors can incur additional fees and prolong transaction durations.
Steps for Using SWIFT Codes
To initiate an international transfer to Banque du Caire, follow these steps:
- Gather recipient details : Collect the recipient's full name, account number, and the SWIFT code ( BCAIEGCX011 ).
- Select a transfer method : Choose between bank wire transfers, online platforms, or other remittance services.
- Complete the application : Fill out the transfer form meticulously, double-checking the SWIFT code.
- Verify fees : Confirm transaction costs with your bank or service provider to avoid unexpected charges.
- Execute the transfer : Submit the request and await confirmation from the recipient's bank.
- Monitor the transaction : Track the transfer to ensure successful completion within the expected timeframe.
Conclusion
SWIFT codes are indispensable in international banking, particularly for institutions like Banque du Caire. Familiarity with their structure and application empowers individuals and businesses to conduct cross-border transactions confidently. Whether for personal or commercial purposes, using the correct SWIFT code— BCAIEGCX011 —ensures secure, efficient, and hassle-free fund transfers. In an interconnected world, mastering these financial tools is not just an advantage but a necessity for seamless global transactions.