In international financial transactions, SWIFT/BIC codes play a pivotal role. Have you ever been uncertain about how to accurately send funds across borders? Understanding the structure of SWIFT/BIC codes can help streamline international wire transfers and minimize errors.
Decoding the SWIFT/BIC Structure
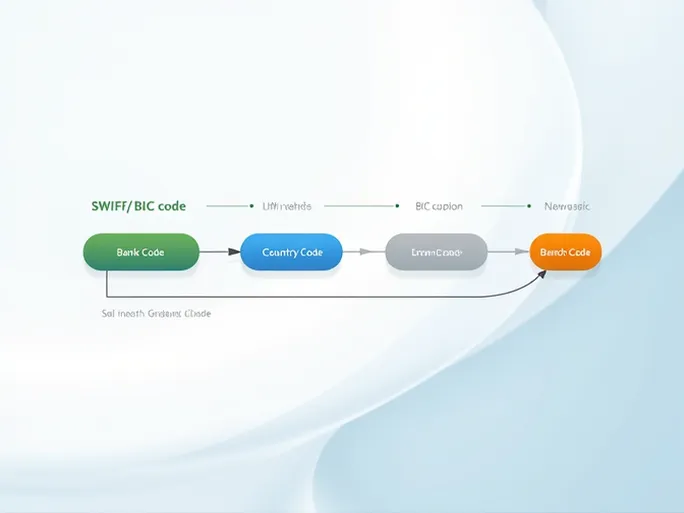
A standard SWIFT/BIC code consists of 8 to 11 characters, divided into distinct sections:
- Bank Code (4 characters) : Identifies the financial institution (e.g., "ESSE" for Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken AB).
- Country Code (2 characters) : Specifies the bank's registered country (e.g., "SE" for Sweden).
- Location Code (2 characters) : Indicates the bank's headquarters city.
- Branch Code (3 characters, optional) : Identifies specific branches, with "XXX" typically representing the head office.
Essential Verification Steps for International Transfers
When initiating cross-border payments, verifying the following details can prevent processing delays and failed transactions:
- Bank Name Accuracy : Confirm the recipient bank's name matches the SWIFT code exactly.
- Branch Specificity : When using branch-specific codes, ensure alignment with the recipient's actual branch.
- Country Validation Double-check that the country code corresponds to the destination country.
In today's interconnected financial landscape, precise information transmission forms the foundation of secure payments. A thorough understanding of SWIFT/BIC codes enables more efficient international transactions and safeguards financial assets against avoidable errors.